Introduction
Recognizing the nuances of food allergies in the workplace is essential for fostering a safe and productive environment. Among these allergies, soy allergies present a unique challenge, affecting a significant portion of the population and leading to various symptoms that can disrupt daily activities. This article explores the ten key soy allergy symptoms that every HR manager should be aware of, offering insights into how these reactions can impact employee well-being and productivity.
What occurs when a seemingly innocuous ingredient like soy becomes a source of distress for employees? Furthermore, how can HR professionals effectively respond to ensure safety and support?
Skin Reactions: Rashes and Hives from Soy Allergy
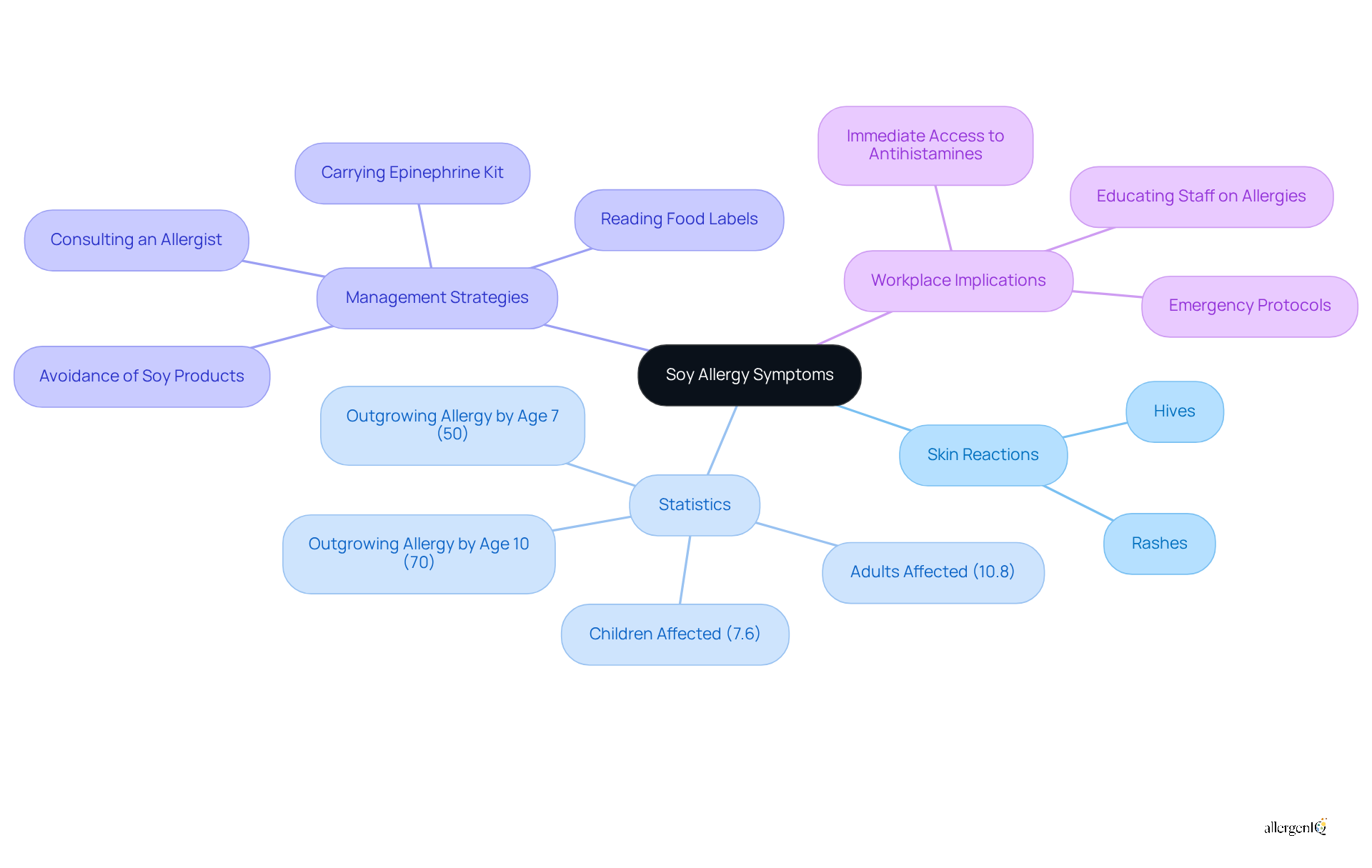
Individuals with a sensitivity to soy frequently experience soy allergy symptoms, particularly rashes and hives. These reactions, which can manifest as raised, red, itchy welts shortly after exposure to soy products, are known as soy allergy symptoms. Soy allergy symptoms are not only common but can significantly impact a person's quality of life and workplace productivity. Research indicates that individuals with soy sensitivities frequently experience soy allergy symptoms, including common skin reactions and mild manifestations like hives. Approximately 7.6% of children and 10.8% of adults in the U.S. are affected by food allergies, with soy identified as one of the most common allergens.
Real-world examples underscore the necessity of recognizing soy allergy symptoms for timely medical intervention. For instance, an employee who develops hives as soy allergy symptoms after consuming a meal containing soy may require immediate access to antihistamines or an epinephrine kit, particularly if they have a history of severe reactions. Dermatologists stress that while mild soy allergy symptoms can often be managed with over-the-counter treatments, severe cases may escalate to anaphylaxis, necessitating emergency care. It is imperative to call 911 after administering an epinephrine shot, regardless of the patient's immediate condition, to ensure proper medical evaluation.
Recent studies have shown that skin-prick tests and specific IgE blood tests are effective in diagnosing soy sensitivities, aiding in the confirmation of allergic responses. Furthermore, AllergenIQ’s comprehensive environmental allergy testing services can assist in identifying common allergens, including soy, which is crucial for effective management strategies. HR managers should encourage staff to read food labels and inquire about ingredients to prevent exposure to soy products. Understanding these indicators, along with the legal framework established by the Food Allergen Labeling & Consumer Protection Act, is essential for HR managers. This knowledge enables them to provide appropriate assistance and resources for affected employees, thereby promoting a safer workplace environment.
Digestive Issues: Nausea and Diarrhea Linked to Soy Allergy
Nausea and diarrhea are common digestive issues associated with soy sensitivities. Employees may experience symptoms, known as soy allergy symptoms, such as:
- Stomach cramps
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
shortly after consuming soy products. It is essential for HR managers to recognize these symptoms to provide appropriate support and maintain a safe work environment.
With one-third of the workforce affected by seasonal and food sensitivities, as well as conditions like eczema and asthma, acknowledging the influence of these issues on employee productivity is crucial.
AllergenIQ's integrated strategy for comprehensive sensitivity management customizes treatment and organizes assistance, effectively alleviating the impacts of sensitivities in the workplace.
Respiratory Distress: Wheezing and Shortness of Breath from Soy Allergy
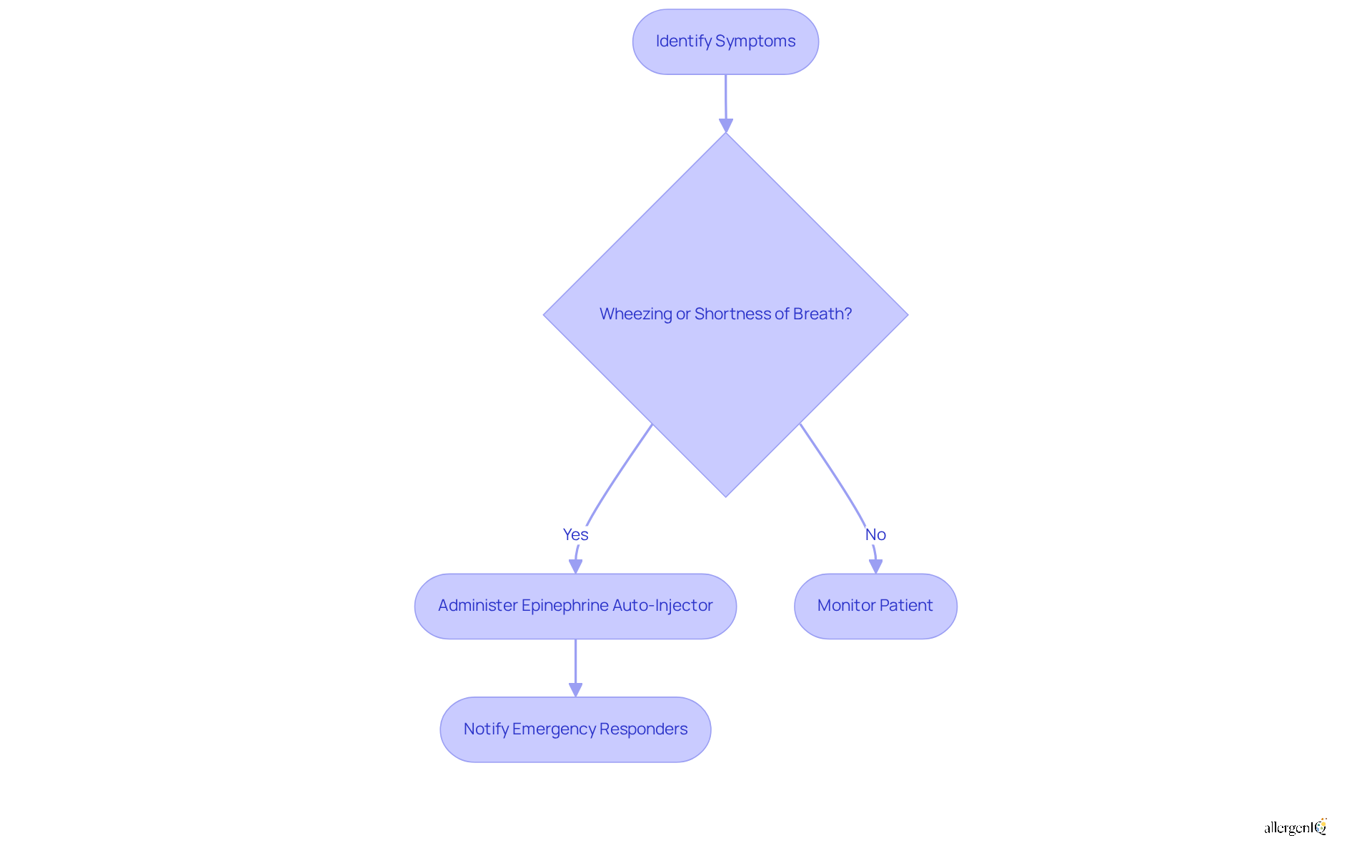
Wheezing and shortness of breath are critical indicators that may manifest as soy allergy symptoms in individuals with a soy intolerance, typically occurring after exposure to soy products. These respiratory issues can escalate rapidly, resulting in considerable difficulty in breathing. Studies reveal that 94% of cases involving allergic reactions to soy report soy allergy symptoms such as shortness of breath. Given the potential severity of these symptoms, it is essential for HR managers to establish effective emergency protocols.
Expert guidance underscores the necessity of having a documented emergency action plan for individuals with soy allergies. This plan should include explicit instructions for identifying and managing respiratory issues during work activities. For example, if an employee displays wheezing or shortness of breath, immediate access to an epinephrine auto-injector is vital, as it serves as the first-line treatment for severe allergic reactions.
Furthermore, the prevalence of respiratory issues among patients experiencing soy allergy symptoms highlights the need for vigilance. A considerable number of individuals may experience wheezing, which can be aggravated by cross-contact with soy in shared cooking environments, resulting in soy allergy symptoms. HR managers must ensure that staff are trained to recognize these symptoms and respond appropriately, including notifying emergency responders if epinephrine has been administered.
Implementing comprehensive emergency protocols not only safeguards the health of staff but also fosters a supportive workplace environment. By prioritizing awareness and preparedness, organizations can effectively manage the risks associated with soy sensitivities and ensure the well-being of their workforce.
Anaphylaxis: Life-Threatening Reaction to Soy Allergy
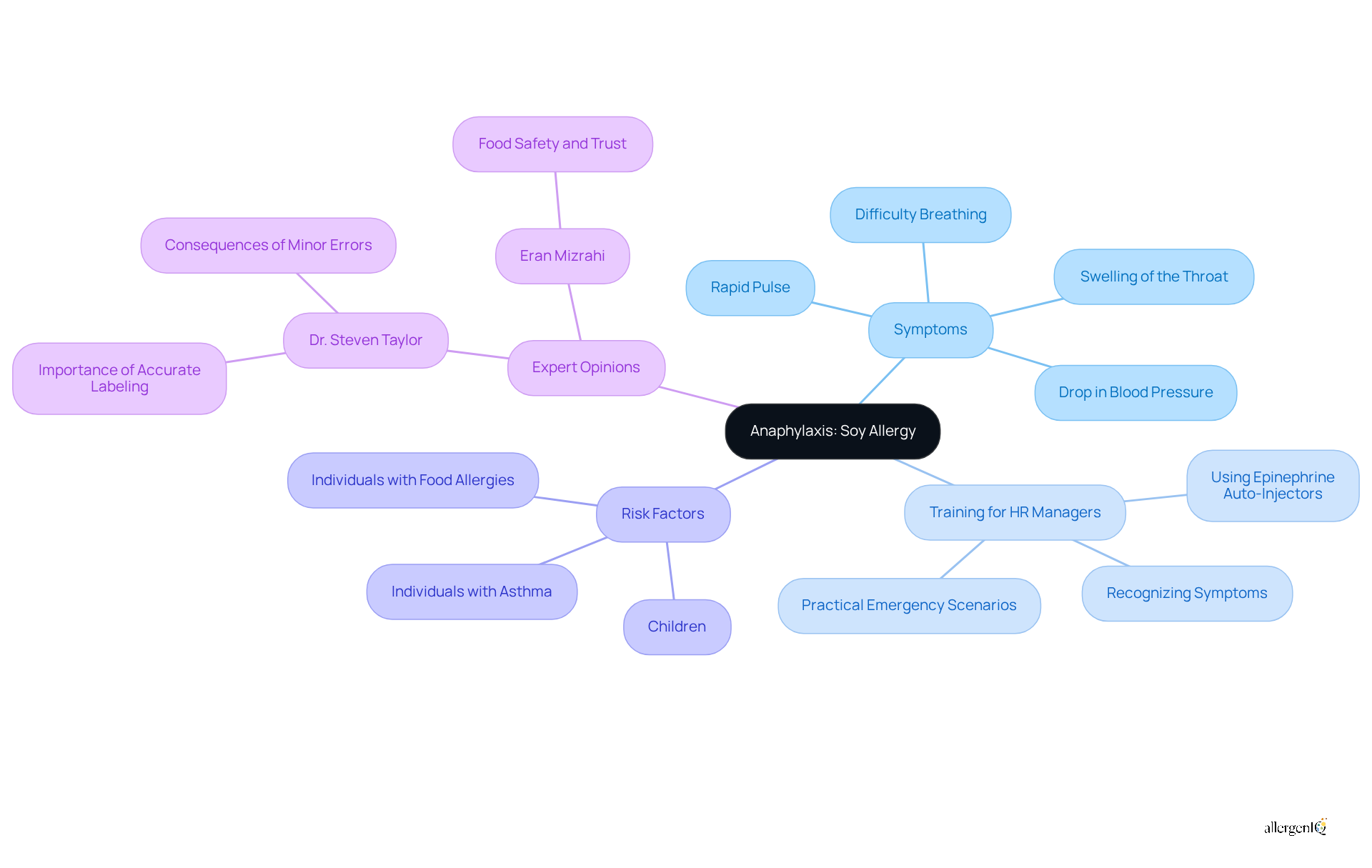
Anaphylaxis is a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction that can be triggered by soy. Soy allergy symptoms may include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the throat
- Rapid pulse
- A significant drop in blood pressure
Given that over 25% of U.S. adults experience sensitivities, it is crucial for HR managers to implement training programs that educate employees on recognizing the symptoms of anaphylaxis and the appropriate emergency responses. This training should ensure that all staff are familiar with the use of epinephrine auto-injectors, which are vital for treating anaphylactic reactions.
While the occurrence of anaphylactic reactions to soy allergy symptoms is less common than reactions to certain other allergens, it still poses a significant risk, particularly for individuals with a documented history of food sensitivities. Experts indicate that those most at risk include individuals with diagnosed food allergies, especially children and those with asthma. Dr. Steven Taylor, a leading authority in food science, underscores that even minor labeling errors can have serious consequences for allergic consumers, highlighting the necessity of vigilance in food safety practices.
HR managers should prioritize training that includes practical scenarios for responding to anaphylaxis, ensuring that staff are equipped to act swiftly and effectively in emergencies. This proactive approach not only safeguards the well-being of employees but also fosters a culture of safety and awareness within the workplace.
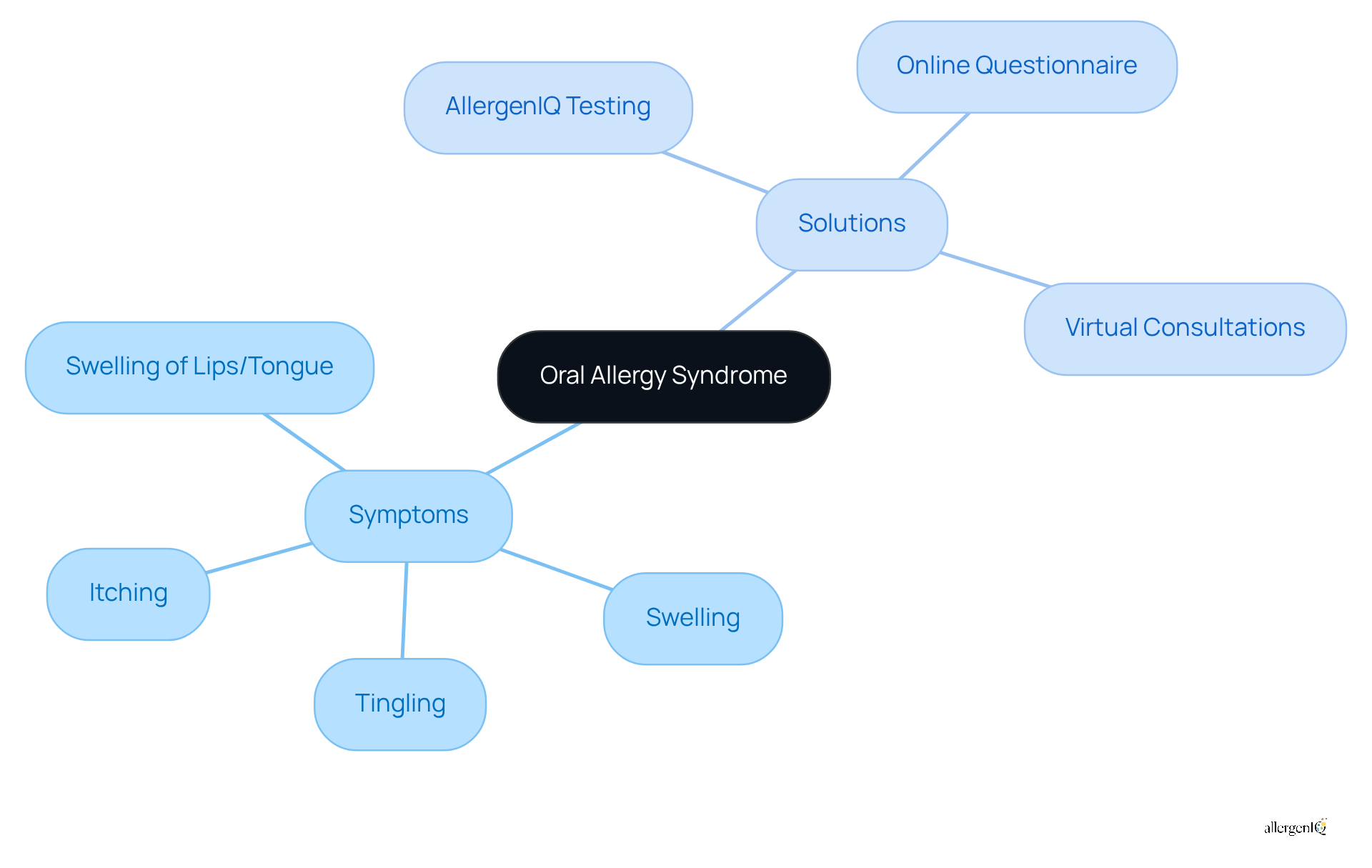
Oral Allergy Syndrome: Itching and Swelling in the Mouth from Soy
Oral hypersensitivity syndrome can result in itching and swelling in the mouth and throat, which are classified as soy allergy symptoms following the consumption of soy products. Common soy allergy symptoms can include tingling sensations and swelling of the lips or tongue. It is crucial for HR managers to encourage staff to report these symptoms, as this facilitates access to appropriate medical advice.
AllergenIQ offers specialized food sensitivity testing that identifies triggers, such as soy, enabling individuals to develop a clear strategy for avoiding harmful foods while maintaining a balanced diet. By utilizing AllergenIQ's comprehensive testing process - which includes a detailed online questionnaire and virtual consultations with specialists - employees can receive personalized treatment plans and ongoing support tailored to their specific triggers.
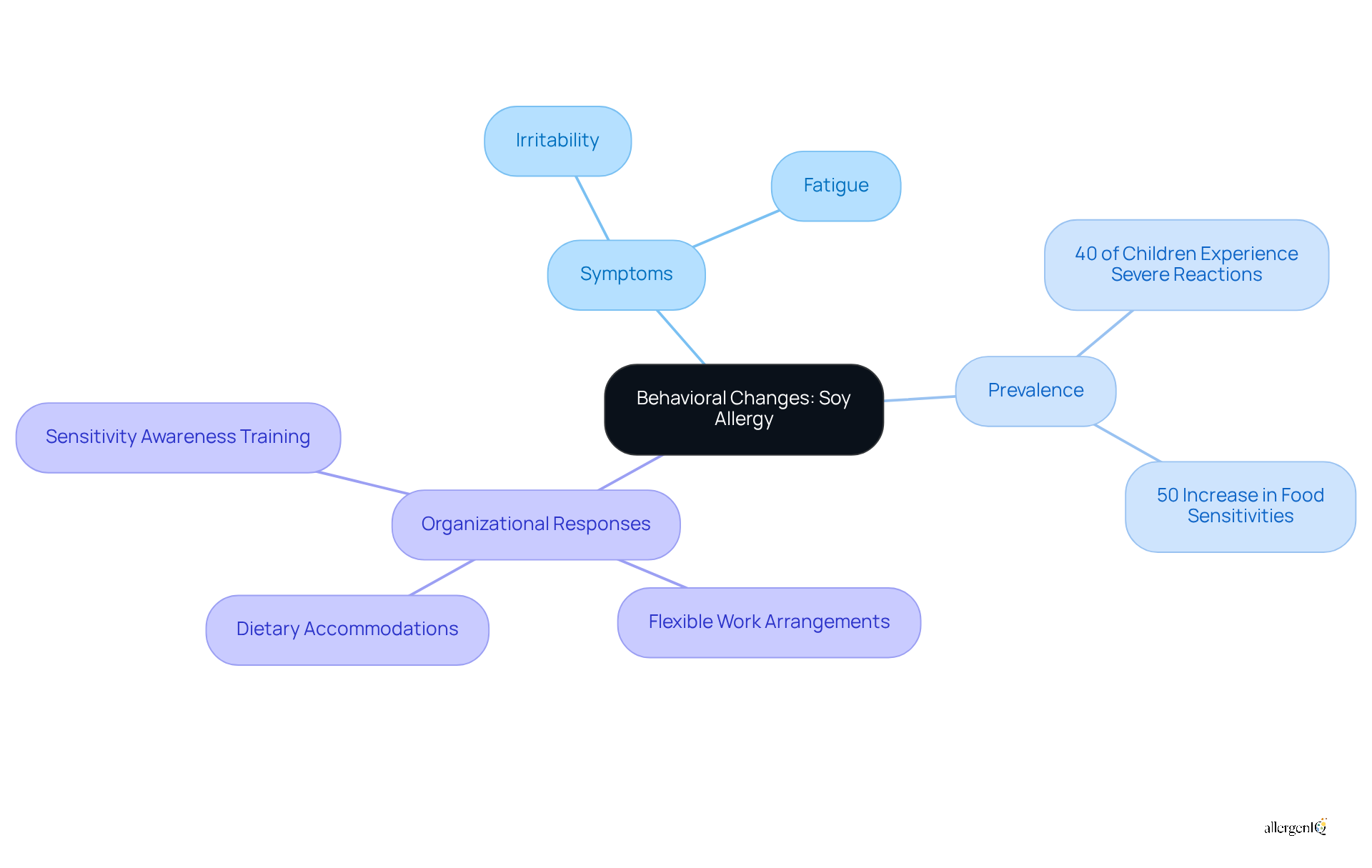
Behavioral Changes: Irritability and Fatigue Associated with Soy Allergy
Employees with a soy sensitivity frequently report irritability and fatigue as significant soy allergy symptoms that indicate their immune responses. These behavioral changes can severely affect workplace productivity and overall morale. Research indicates that irritability and fatigue are prevalent among individuals who experience soy allergy symptoms. Studies reveal that over 40 percent of children with such conditions have experienced severe reactions, including emotional disturbances. Moreover, the prevalence of food sensitivities among children has increased by 50 percent over the past two decades, underscoring the urgent need for awareness in the workplace.
According to FARE, approximately 33 million individuals in the United States have at least one food sensitivity, highlighting the widespread nature of this issue. Notably, one third of the workforce is affected by seasonal and food sensitivities, eczema, and asthma, which can lead to diminished focus and engagement, ultimately influencing team dynamics and output. HR managers must recognize that these symptoms can result in decreased concentration and participation, thereby impacting overall team performance.
To address these challenges, organizations should implement supportive measures such as:
- Flexible work arrangements
- Access to snacks that accommodate dietary restrictions
- Educational resources regarding food sensitivities
Programs like sensitivity awareness training for staff can foster a more inclusive atmosphere, ensuring that individuals with soy allergy symptoms feel acknowledged and supported. By proactively addressing these behavioral changes, organizations can enhance employee well-being and sustain productivity.
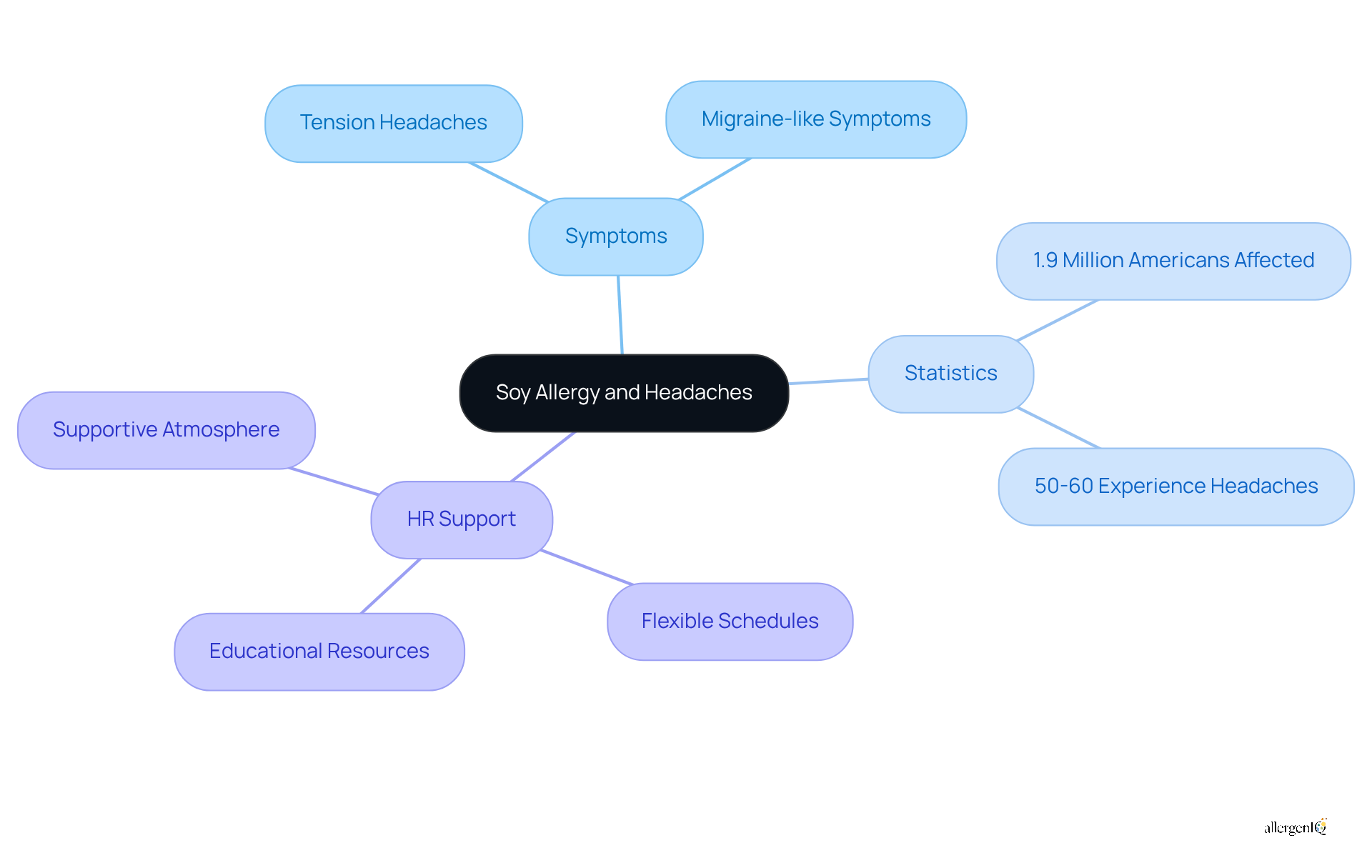
Headaches: A Possible Reaction to Soy Allergy
Headaches can significantly indicate soy sensitivities, often manifesting as tension headaches or migraine-like symptoms. Approximately 1.9 million Americans report symptoms related to soy food sensitivities, with many misinterpreting their reactions as food intolerances. For individuals who frequently experience headaches after consuming soy, seeking medical advice for accurate diagnosis and management is essential. Specialists, including allergists, emphasize the importance of professional assessment, as true food sensitivities require comprehensive testing, frequently culminating in an oral food challenge.
Human Resources (HR) managers can play a crucial role in supporting employees experiencing these symptoms by cultivating an environment that prioritizes health and wellness. This may involve:
- Implementing workplace policies that allow flexible schedules for medical appointments
- Providing educational resources on food sensitivities
- Creating a supportive atmosphere where employees feel comfortable discussing their health issues
Statistics indicate that headaches occur in 50% to 60% of individuals with soy sensitivities, underscoring the need for workplace awareness and support. By understanding the implications of soy sensitivities and their potential indicators, HR managers can more effectively assist employees in managing their health issues, ultimately promoting a healthier and more productive work environment.
Swelling: Facial and Throat Swelling from Soy Allergy
Facial and throat swelling can occur in individuals with a soy intolerance, often indicating soy allergy symptoms that suggest a serious allergic response. Symptoms of a soy allergy may include swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat, potentially leading to difficulty breathing. Notably, individuals with food sensitivities are two to four times more likely to experience additional health issues, such as atopic dermatitis, rhinitis, or asthma, compared to those without food sensitivities. These conditions can exacerbate the soy allergy symptoms that are associated with soy intolerance.
To effectively manage these risks, HR managers should ensure that staff are informed about AllergenIQ’s comprehensive environmental sensitivity testing services. These services can identify reactions to common airborne irritants, including pollen, dust mites, and pet dander. By understanding these allergens, individuals can develop strategies to minimize exposure and manage symptoms throughout the year.
It is essential to establish clear protocols for emergency situations, such as ensuring the availability of self-injectable epinephrine devices, which are obtainable by prescription. This measure can be lifesaving in critical moments. Furthermore, fostering an environment where employees feel comfortable disclosing their sensitivities and any related symptoms is vital. By promoting awareness and preparedness, HR managers can significantly mitigate the risks associated with soy allergy symptoms in the workplace.
Dizziness: Lightheadedness as a Soy Allergy Symptom
Dizziness or lightheadedness can occur in individuals with a soy sensitivity, often as a result of soy allergy symptoms from a severe allergic response. Given that approximately one-third of the workforce may be affected by seasonal and food sensitivities, eczema, and asthma, it is crucial for HR managers to recognize these symptoms. They should encourage individuals experiencing such symptoms to seek medical attention. Being prepared to assist in these situations not only promotes employee well-being but also addresses the broader impact of sensitivities on workplace productivity.
Consult AllergenIQ: Expert Support for Managing Soy Allergy Symptoms
AllergenIQ provides comprehensive support for individuals managing soy allergies. The service includes personalized virtual consultations, allowing staff to receive tailored advice and treatment plans aimed at effectively managing symptoms such as frequent sneezing, congestion, and gastrointestinal issues. These consultations deliver the same high-quality care as in-person visits, with the added benefit of remote access, facilitating easier assistance for individuals.
HR managers play a crucial role in promoting the availability of these resources. By doing so, they ensure employee well-being and empower staff with ongoing allergy support, which can significantly enhance overall productivity.
Conclusion
Understanding soy allergy symptoms is essential for HR managers aiming to cultivate a safe and supportive workplace. By being aware of the various manifestations of soy allergies - ranging from skin reactions and digestive issues to respiratory distress and anaphylaxis - HR professionals can implement measures that protect employees and promote overall well-being.
This article outlines ten key symptoms associated with soy allergies, underscoring the importance of recognizing these signs for timely intervention. It stresses the necessity of effective emergency protocols, urging staff to remain vigilant and prepared for potential allergic reactions. Training programs and resources, such as those provided by AllergenIQ, play a crucial role in equipping employees with the knowledge needed to manage their sensitivities effectively.
Ultimately, prioritizing awareness and education regarding soy allergies enables organizations to foster a more inclusive atmosphere that acknowledges the challenges faced by affected employees. This commitment not only enhances individual health but also contributes to a more productive and engaged workforce, highlighting the significance of understanding and addressing food sensitivities in the workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common skin reactions associated with soy allergy?
Common skin reactions include rashes and hives, which manifest as raised, red, itchy welts shortly after exposure to soy products.
How prevalent are soy allergies among the population?
Approximately 7.6% of children and 10.8% of adults in the U.S. are affected by food allergies, with soy being one of the most common allergens.
What should be done if someone experiences severe soy allergy symptoms, such as hives?
If someone develops hives after consuming soy, they may require immediate access to antihistamines or an epinephrine kit, especially if they have a history of severe reactions. It is important to call 911 after administering an epinephrine shot for proper medical evaluation.
How can soy allergies be diagnosed?
Soy allergies can be diagnosed using skin-prick tests and specific IgE blood tests, which help confirm allergic responses.
What digestive issues are commonly linked to soy allergies?
Common digestive issues associated with soy allergies include nausea, stomach cramps, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Why is it important for HR managers to recognize symptoms of soy allergies?
Recognizing symptoms is crucial for HR managers to provide appropriate support and maintain a safe work environment, especially since one-third of the workforce may be affected by food sensitivities.
What respiratory symptoms can indicate a soy allergy?
Respiratory symptoms that may indicate a soy allergy include wheezing and shortness of breath, which can occur after exposure to soy products.
What emergency protocols should be established for individuals with soy allergies?
HR managers should have a documented emergency action plan that includes instructions for identifying and managing respiratory issues, ensuring immediate access to an epinephrine auto-injector for severe allergic reactions.
How can organizations support employees with soy sensitivities?
Organizations can support employees by encouraging them to read food labels, inquire about ingredients, and implement comprehensive emergency protocols to manage the risks associated with soy sensitivities effectively.




