Introduction
Recognizing the symptoms of gluten allergy is essential as dietary sensitivities become more common. Symptoms can range from digestive distress to neurological issues, significantly affecting individuals' quality of life. Many people experience these symptoms without understanding their underlying cause, raising the question: how can one distinguish between simple discomfort and a serious gluten intolerance? This article explores ten key symptoms of gluten allergy, equipping readers with the knowledge to identify their experiences and seek appropriate assistance.
Digestive Distress: Bloating and Gas
Bloating and gas frequently indicate symptoms of allergy to gluten, which manifest as a sensation of fullness or swelling in the abdomen after consuming foods containing this protein. This discomfort often accompanies excessive gas, leading to social embarrassment and anxiety. Recent research indicates that approximately 74% of individuals who self-report reactions to gluten experience bloating, while 49% report symptoms of allergy to gluten, including abdominal discomfort. Furthermore, a significant portion of these individuals (73.5%) have noted that their symptoms worsen with high FODMAP-containing products, suggesting that fermentable carbohydrates may exacerbate their digestive issues.
Notably, 47% of those with self-reported reactions to specific proteins have attempted a gluten-free or restricted diet, reflecting the measures taken by individuals facing these challenges. Current research underscores the necessity of recognizing these digestive issues, as they can profoundly affect quality of life and daily functioning. Additionally, 84% of individuals with self-reported intolerance to wheat proteins have indicated a correlation between increased abdominal issues and stress, highlighting the psychological factors involved in managing wheat intolerance.
By identifying and addressing the symptoms of allergy to gluten, individuals can take informed steps toward managing their health and well-being. The wheat-free market, valued at $11 billion, underscores the growing awareness and economic impact of wheat sensitivity.
Skin Reactions: Rashes and Eczema
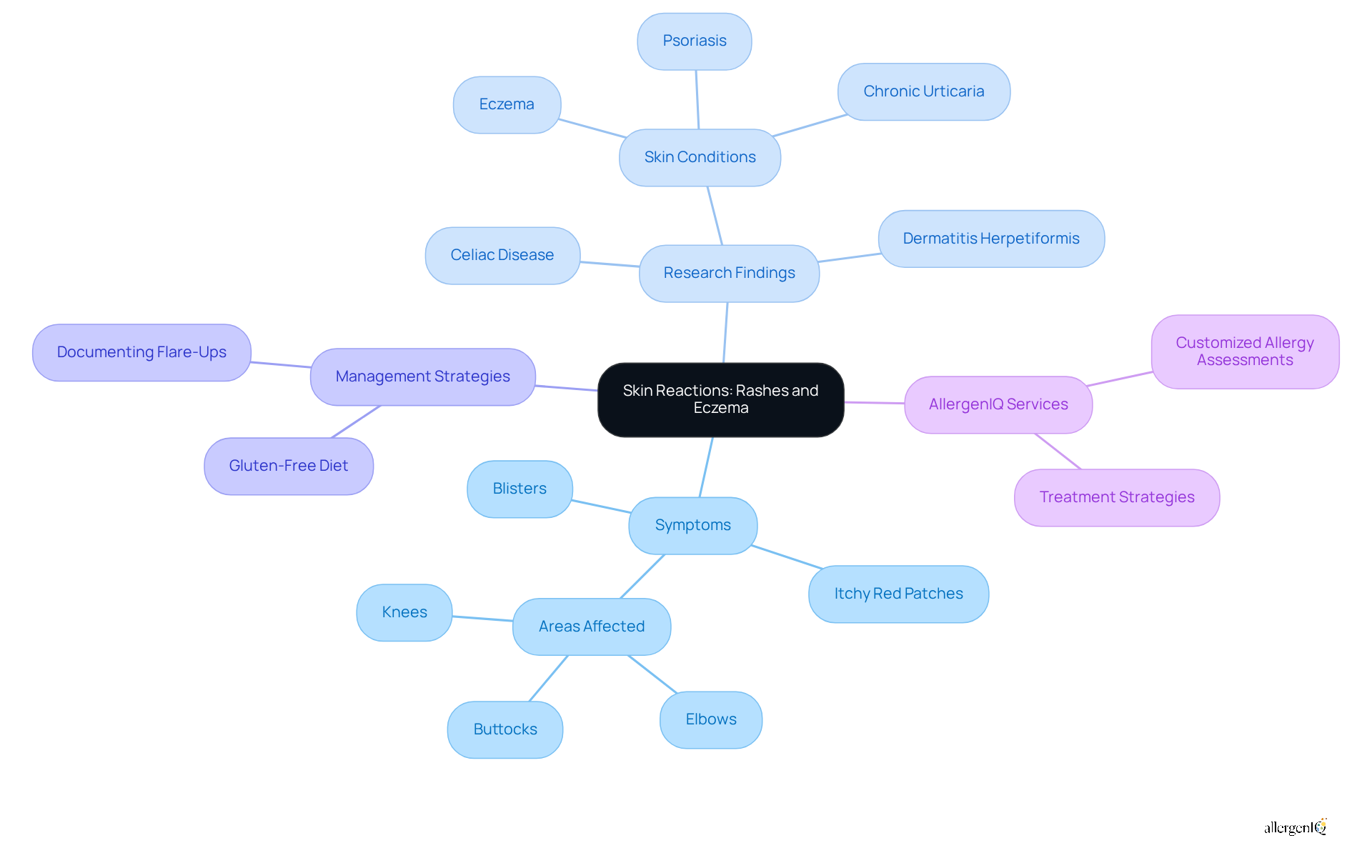
Individuals with wheat sensitivity frequently experience skin reactions, particularly rashes and eczema. These conditions typically manifest as itchy, red patches or blisters, especially on areas such as the elbows, knees, and buttocks. Research indicates that up to 20% of individuals with celiac disease may initially exhibit skin manifestations, such as dermatitis herpetiformis, rather than gastrointestinal issues. This highlights the importance of recognizing the connection between skin symptoms and the symptoms of allergy to gluten.
Recent studies have established a significant correlation between gluten-related disorders and various skin conditions, including eczema, psoriasis, and chronic urticaria. For example, patients with celiac disease have been found to have higher rates of skin diseases compared to control groups, with increased risks for conditions like atopic dermatitis. This suggests that wheat sensitivity may present through persistent skin problems, complicating both diagnosis and treatment.
Dermatologists emphasize the necessity of awareness regarding certain dietary components as potential contributors to unexplained chronic skin conditions. Effective management strategies often involve adhering to a strict gluten-free diet, which has been shown to significantly improve the symptoms of allergy to gluten and skin conditions. By documenting flare-ups and discussing dietary habits with healthcare professionals, individuals can more effectively manage their reactions and enhance their overall quality of life.
At AllergenIQ, we provide customized allergy assessments and treatment strategies designed to identify specific allergens and assist individuals in managing their reactions effectively. Through case studies from our clients, we illustrate how tailored approaches can lead to substantial improvements in skin health and overall well-being.
Neurological Symptoms: Headaches and Brain Fog
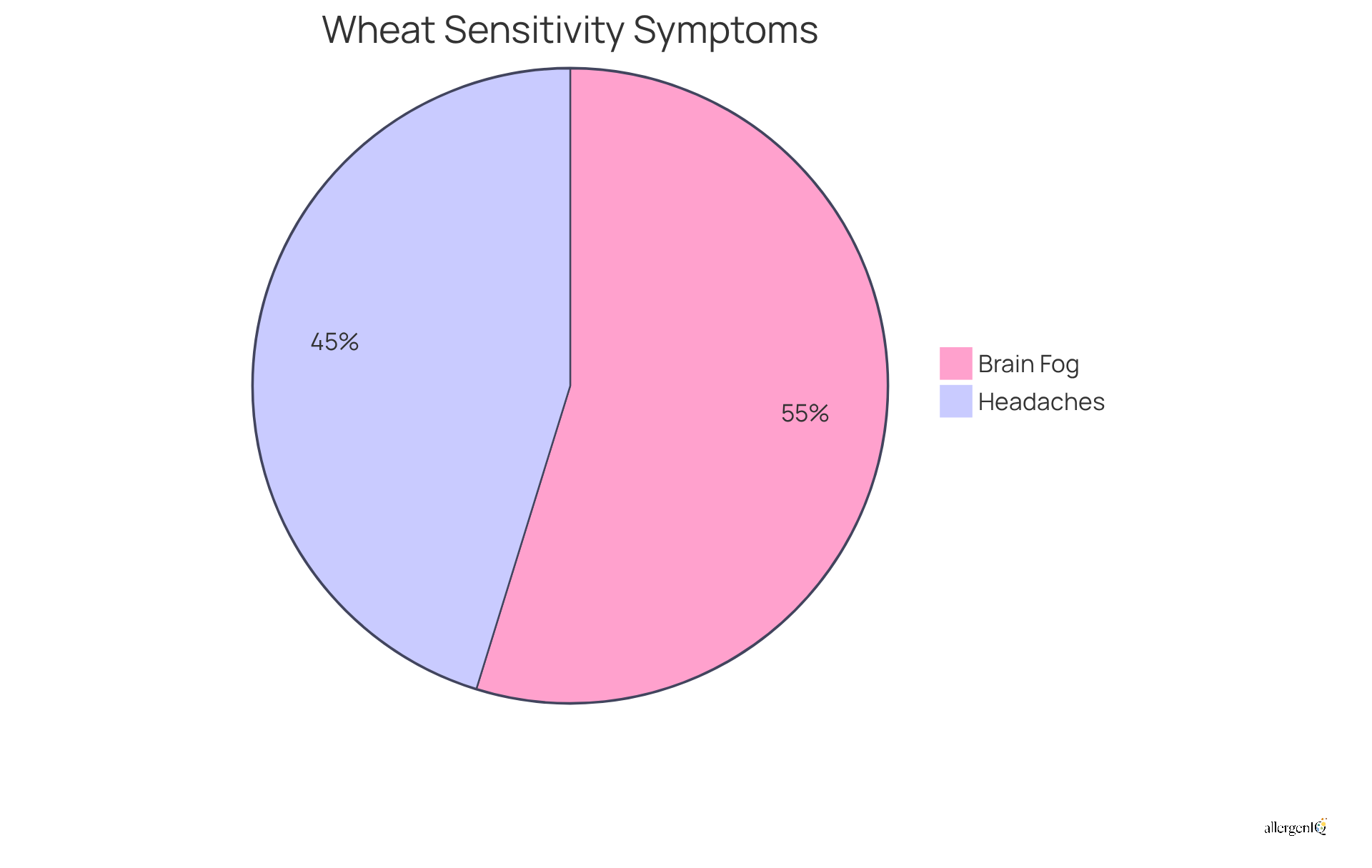
Individuals with wheat intolerance frequently experience neurological issues, notably headaches and mental cloudiness. These symptoms can manifest as difficulties in concentration, forgetfulness, and a pervasive sense of mental fatigue. Recent research indicates that approximately 71% of individuals sensitive to wheat report headaches following exposure, with many experiencing these symptoms within two hours of consumption. Furthermore, a study revealed that 86% of participants noted brain fog or concentration difficulties after consuming wheat, highlighting the cognitive impact associated with this sensitivity.
Real-world examples further illustrate the significant effects of these symptoms on daily life. Parents of children with wheat sensitivities often observe marked improvements in academic performance when wheat is eliminated from their diets, suggesting a direct correlation between dietary choices and cognitive function. Additionally, numerous individuals report that their headaches and brain fog considerably impede their productivity and overall quality of life.
Psychologists emphasize the importance of recognizing the dietary influences on mental well-being, noting that the intake of certain proteins may exacerbate symptoms of anxiety and depression. A comprehensive understanding of the gut-brain connection is crucial for the effective management of wheat sensitivity. As awareness grows, individuals are empowered to make informed dietary adjustments that could mitigate these cognitive challenges, ultimately enhancing their daily functioning and overall well-being. It is also essential to seek medical attention if headaches are sudden and extremely severe, as this may indicate a more serious condition.
Gastrointestinal Issues: Diarrhea
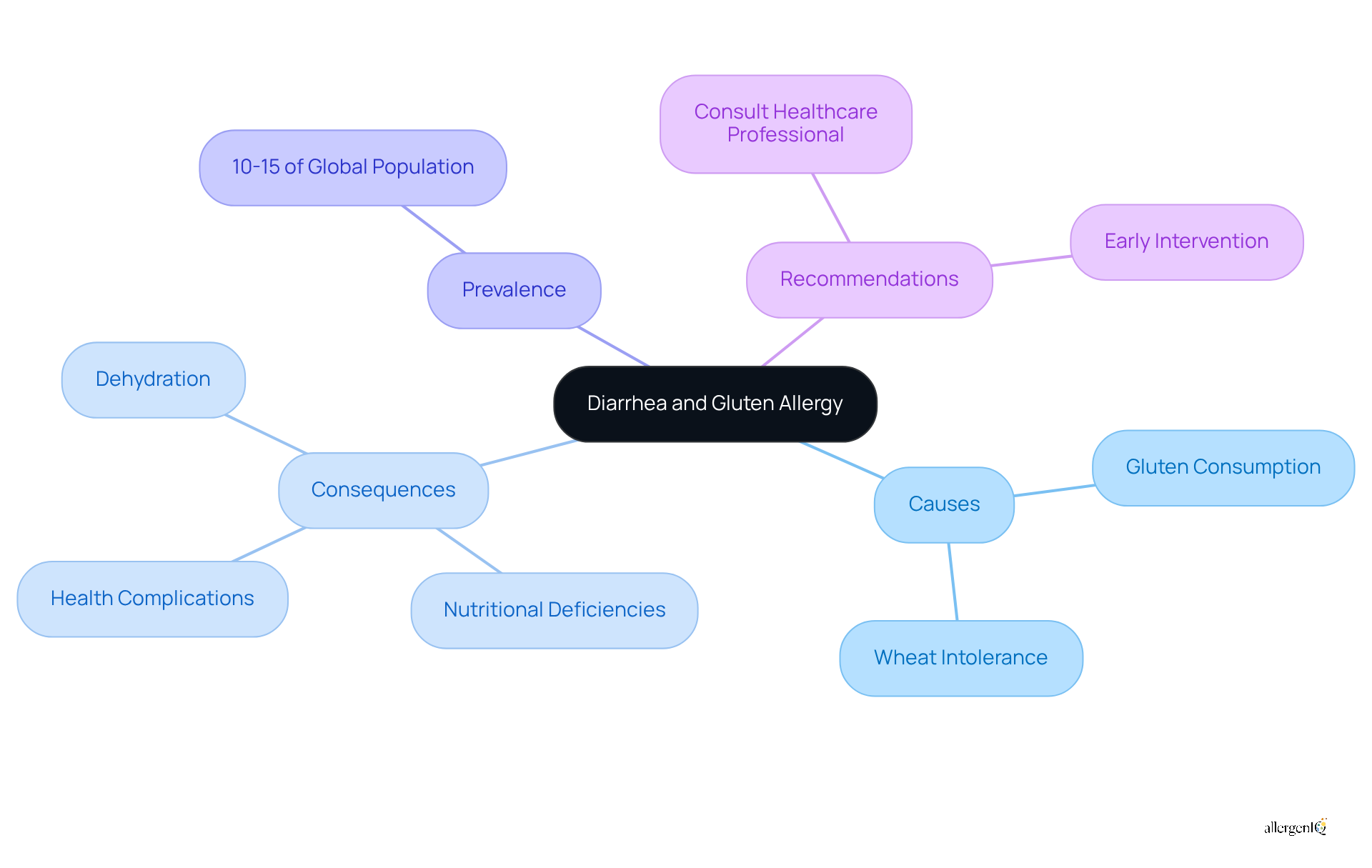
Diarrhea is one of the symptoms of allergy to gluten, frequently occurring after the consumption of gluten-containing foods. If not managed appropriately, this condition can lead to dehydration and nutritional deficiencies. Recent studies indicate that gastrointestinal issues, including diarrhea, bloating, and constipation, can be symptoms of allergy to gluten, which are common among individuals with wheat intolerance and adversely affect their overall health and nutrition. For example, chronic diarrhea may result in malabsorption of vital nutrients, such as iron and vitamin B12, which can lead to deficiencies that impact growth and development, particularly in children.
Non-celiac gluten intolerance (NCGI) affects approximately 10-15% of the global population, emphasizing the importance of identifying the symptoms of allergy to gluten. Individuals experiencing persistent diarrhea should seek consultation with a healthcare professional to evaluate the potential for wheat sensitivity, as accurate diagnosis is essential prior to making dietary modifications. Early intervention is critical, as untreated food intolerance can lead to severe health complications, including an increased risk of developing various types of cancer.
Chronic Fatigue: Low Energy Levels
Chronic fatigue frequently affects individuals with wheat sensitivity, as they experience symptoms of allergy to gluten, which manifest as a persistent sense of exhaustion that significantly disrupts daily activities and diminishes overall quality of life. Research indicates that the prevalence of fatigue among patients with celiac disease can range from 8% to 100%, underscoring the variability in experiences related to wheat consumption. A study involving 78 celiac disease patients found that after one year on a gluten-free diet, the median fatigue severity scores decreased from 3.8 to 1.9, reflecting substantial improvement; however, fatigue levels remained elevated compared to healthy controls. This suggests that while dietary changes can alleviate some symptoms, they may not fully resolve the fatigue associated with wheat sensitivity.
Health professionals emphasize the importance of recognizing the symptoms of allergy to gluten and their connection to energy levels. Berit Mære Skjellerudsveen highlights that fatigue is a common complaint among celiac disease patients, and unexplained fatigue should prompt clinicians to consider the symptoms of allergy to gluten as a potential diagnosis. This connection is vital, as untreated celiac disease can lead to malabsorption, which can cause symptoms of allergy to gluten, further intensifying fatigue.
Real-world examples illustrate the impact of gluten on energy levels. Many individuals report experiencing symptoms of allergy to gluten, including fatigue after consuming gluten-rich foods, which can impede their ability to perform daily tasks, from work obligations to family interactions. The emotional toll of chronic fatigue can also lead to increased stress and anxiety, complicating the management of food intolerance. Notably, up to 40% of patients encounter challenges in adhering to a gluten-free diet, significantly affecting their quality of life.
Recent research underscores the necessity for more comprehensive studies to investigate the mechanisms underlying fatigue in celiac disease and wheat sensitivity. Understanding these connections can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices and seek appropriate medical advice, ultimately improving their quality of life.
Respiratory Symptoms: Nasal Congestion
Nasal congestion frequently occurs in individuals with wheat sensitivity, often misidentified as seasonal allergies or a cold. This condition can present as a stuffy or runny nose, sneezing, and sinus pressure, leading to discomfort and hindering daily activities. Recent findings indicate that respiratory issues, such as nasal congestion, can be directly linked to specific food exposures, underscoring the need for awareness and effective management strategies.
For instance, research shows that approximately 7.8 million children in the U.S. suffer from respiratory allergies, with many potentially experiencing issues related to gluten. Allergists stress the importance of recognizing these respiratory problems as possible indicators of wheat sensitivity, advocating for a thorough assessment of dietary habits in patients exhibiting symptoms of allergy to gluten.
By understanding the connection between wheat protein and nasal blockage, individuals can take informed steps to manage their health effectively.
Mood Changes: Anxiety and Depression
Individuals with wheat sensitivity often experience mood fluctuations, including anxiety and depression. These symptoms may stem from the body's inflammatory response to specific proteins, which can adversely affect mental health. Recognizing this link is crucial, as it can encourage individuals to seek appropriate support and make necessary dietary changes.
Joint Pain: Inflammation and Discomfort
Joint discomfort is a prevalent issue for individuals with wheat sensitivity, often presenting as swelling and rigidity in major joints, which can significantly hinder movement. Recent research indicates that specific proteins may trigger a low-grade inflammatory response in sensitive individuals, worsening existing joint discomfort. Notably, studies reveal that approximately 10.7% of patients with celiac disease report joint complaints, underscoring that these symptoms can manifest as extra-intestinal issues in patients with Celiac Disease (CD) who do not have rheumatic comorbidities. This highlights the importance of recognizing this connection.
Rheumatologists have noted that inflammation linked to certain proteins can aggravate conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis, suggesting that dietary modifications may be beneficial. Evidence shows that a strict diet devoid of wheat proteins can alleviate symptoms in many individuals with celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, often within a span of four to six weeks. For instance, a case study documented a patient whose knee pain and dermatitis herpetiformis improved markedly after transitioning to a gluten-free diet, illustrating the potential of dietary changes to enhance joint health.
Statistics indicate that joint pain can be one of the symptoms of allergy to gluten, even in the absence of digestive issues. With over 50 million adults in the U.S. suffering from joint pain due to arthritis, understanding the role of wheat protein in inflammation is crucial for effective management. However, it is essential to recognize that not all individuals with joint pain should eliminate wheat proteins; this strategy is most appropriate for specific populations. As awareness grows, individuals experiencing unexplained joint discomfort are encouraged to consult healthcare professionals about the possibility of wheat intolerance and the benefits of dietary adjustments.
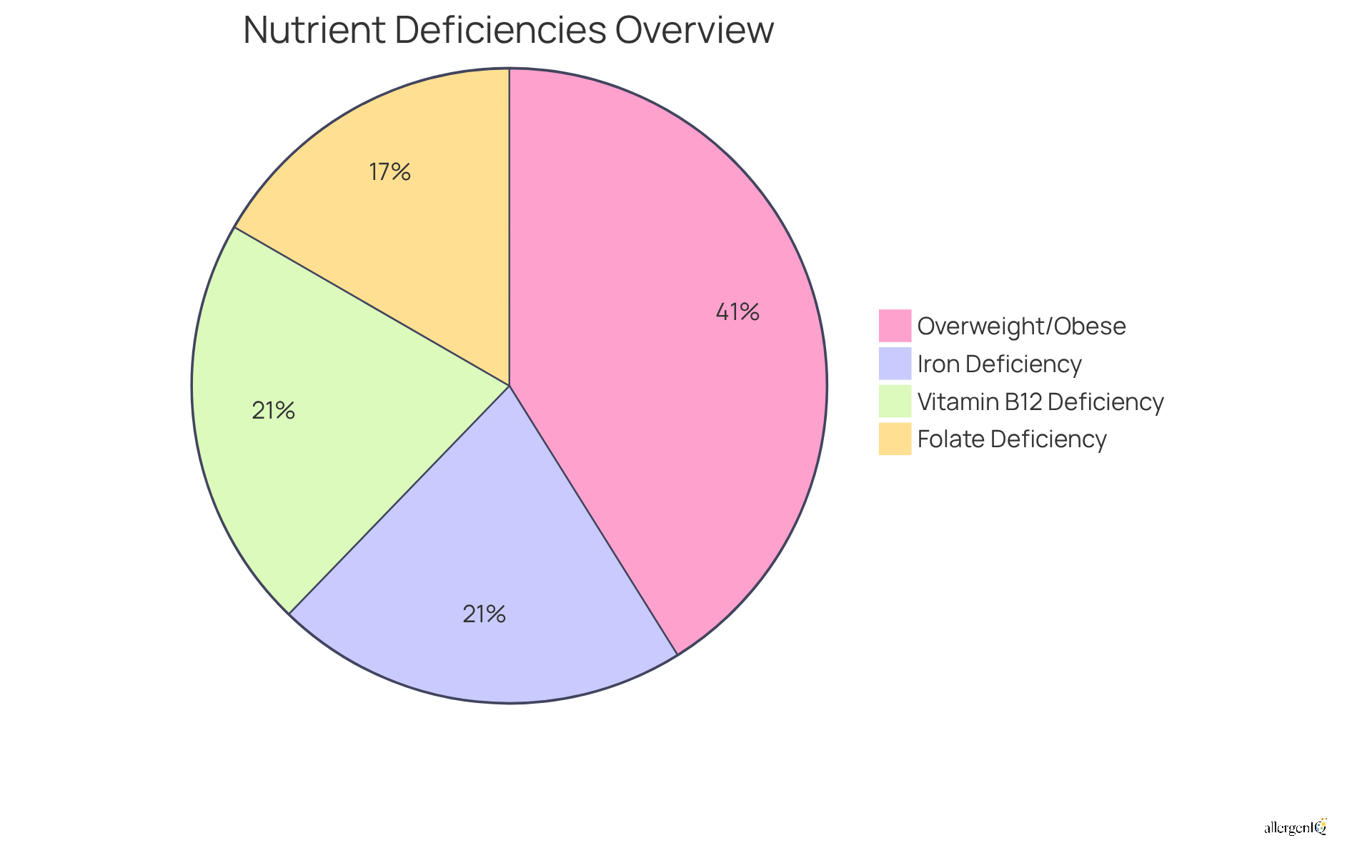
Unexplained Weight Loss: Nutrient Absorption Issues
Unexplained weight loss represents a significant concern for individuals with wheat intolerance, primarily due to the malabsorption of essential nutrients. Research indicates that nutrient deficiencies are common among those diagnosed with celiac disease, with:
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Folate deficiency
frequently observed as extra-intestinal manifestations at the time of diagnosis. Notably, up to 87% of celiac patients present with at least one vitamin or mineral deficiency, underscoring the urgent need for thorough nutritional assessment and intervention.
The incidence of overweight and obesity among newly diagnosed celiac patients has markedly increased, with nearly 37% categorized as overweight or obese at diagnosis. This trend emphasizes the importance of recognizing that symptoms of allergy to gluten can manifest in various ways, including unexplained weight loss or gain, rather than solely through traditional symptoms like diarrhea or malnutrition.
Nutritionists emphasize that adhering to a balanced diet devoid of wheat proteins is essential for individuals with gluten intolerance to prevent further complications, including an elevated risk of metabolic syndrome. As one specialist noted, "Patients should focus not only on avoiding gluten-free options but also on ensuring their diet is nutritionally adequate to support overall health."
If you experience significant weight loss without an identifiable cause, it is imperative to consult a healthcare professional to rule out the symptoms of allergy to gluten. They can assist in exploring the possibility of wheat sensitivity and recommend appropriate dietary adjustments to effectively address nutrient absorption issues.
Seek Help: Consult AllergenIQ for Personalized Allergy Management
If you suspect gluten intolerance, consulting with AllergenIQ can significantly enhance your allergy management experience. Our dedicated team of specialists provides personalized strategies tailored to your unique symptoms, ensuring a comprehensive approach to your health. Through a streamlined online consultation process, patients can easily identify their triggers and receive customized treatment plans that incorporate dietary adjustments and ongoing support.
Recent advancements in allergy management, including the integration of cognitive behavioral therapy to address anxiety related to food allergies, empower individuals to manage their conditions effectively. By reaching out to AllergenIQ, you gain access to expert guidance that can improve your quality of life and help you confidently manage gluten intolerance from the comfort of your home.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of gluten allergy is essential for individuals facing various health challenges. This article outlines ten key symptoms, which include digestive issues such as bloating and gas, as well as neurological concerns like headaches and brain fog. Understanding these symptoms not only aids in identifying potential gluten intolerance but also empowers individuals to take informed steps toward enhancing their health and well-being.
The connections between gluten sensitivity and a wide range of symptoms are clearly established. Skin reactions, gastrointestinal problems, chronic fatigue, respiratory issues, mood fluctuations, joint pain, and unexplained weight loss all exemplify the complex nature of gluten allergies. These symptoms can significantly affect daily life, highlighting the necessity of seeking medical advice and considering dietary adjustments to alleviate discomfort and improve quality of life.
Given the profound impact gluten sensitivity can have on both physical and mental health, it is crucial for individuals experiencing these symptoms to consult healthcare professionals. Personalized allergy management, such as that provided by AllergenIQ, offers tailored strategies to help individuals navigate their dietary requirements and enhance their overall health. By recognizing the signs of gluten intolerance and taking informed actions, individuals can reclaim their well-being and lead a more vibrant life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common digestive symptoms associated with gluten intolerance?
Common digestive symptoms include bloating and gas, which manifest as a sensation of fullness or swelling in the abdomen after consuming gluten-containing foods. Excessive gas can lead to social embarrassment and anxiety.
How prevalent are bloating and gas among individuals who react to gluten?
Approximately 74% of individuals who self-report reactions to gluten experience bloating, while 49% report symptoms of gluten allergy, including abdominal discomfort.
What dietary components may exacerbate digestive issues for those sensitive to gluten?
High FODMAP-containing products may exacerbate digestive issues, as noted by 73.5% of individuals with self-reported reactions to gluten.
What percentage of individuals with gluten sensitivity have tried a gluten-free diet?
About 47% of those with self-reported reactions to specific proteins have attempted a gluten-free or restricted diet to manage their symptoms.
How do psychological factors relate to wheat intolerance symptoms?
Research indicates that 84% of individuals with self-reported intolerance to wheat proteins correlate increased abdominal issues with stress, highlighting the psychological factors involved in managing wheat intolerance.
What skin reactions are commonly associated with wheat sensitivity?
Individuals with wheat sensitivity often experience skin reactions such as rashes and eczema, which manifest as itchy, red patches or blisters, particularly on the elbows, knees, and buttocks.
What skin condition may indicate celiac disease?
Dermatitis herpetiformis is a skin condition that can occur in up to 20% of individuals with celiac disease, often appearing before gastrointestinal symptoms.
What is the correlation between gluten-related disorders and skin conditions?
Studies show a significant correlation between gluten-related disorders and various skin conditions, including eczema, psoriasis, and chronic urticaria, with individuals with celiac disease having higher rates of skin diseases.
How can skin conditions related to gluten sensitivity be managed?
Effective management often involves adhering to a strict gluten-free diet, which has been shown to improve symptoms of allergy to gluten and related skin conditions.
What neurological symptoms are associated with wheat intolerance?
Common neurological symptoms include headaches and mental cloudiness, which can manifest as difficulties in concentration, forgetfulness, and mental fatigue.
How prevalent are headaches among individuals sensitive to wheat?
Approximately 71% of individuals sensitive to wheat report experiencing headaches following exposure, with many noting these symptoms within two hours of consumption.
What impact does eliminating wheat from the diet have on cognitive function?
Parents of children with wheat sensitivities often observe marked improvements in academic performance when wheat is eliminated from their diets, indicating a direct correlation between dietary choices and cognitive function.
What should individuals do if they experience sudden and severe headaches?
It is essential to seek medical attention if headaches are sudden and extremely severe, as this may indicate a more serious condition.




