Introduction
Allergy testing is essential for identifying the triggers of adverse reactions in adults. Two primary methods - skin tests and blood tests - lead the way in diagnostics. Each method presents distinct advantages: skin evaluations yield rapid results, while blood analyses offer convenience for individuals with specific medical conditions. As individuals strive to manage their allergies effectively, a critical question emerges: which testing method provides the most valuable insights for personalized treatment? This article examines the nuances of skin versus blood tests, analyzing their effectiveness, methodologies, and the considerations that can guide individuals toward informed decisions in their allergy management journey.
Understand Allergy Testing: An Overview
Allergy testing for adults is crucial in identifying allergens that provoke adverse reactions in individuals. The two primary methods for evaluating sensitivity are dermal examinations and serum examinations.
- Skin evaluations involve exposing the skin to small quantities of allergens through pricks or scratches.
- Blood analyses assess the immune system's response to allergens by detecting specific IgE antibodies in the bloodstream.
Both approaches aim to deliver accurate diagnoses, which allows healthcare providers to recommend tailored treatment plans that meet individual needs, including those identified through allergy testing for adults.
At AllergenIQ, we enhance this process by offering innovative at-home sensitivity testing that matches the accuracy of in-clinic evaluations. Our method allows individuals to perform tests conveniently from home, followed by personalized consultations with our specialists. After reviewing your responses and symptoms, our specialists formulate customized treatment strategies to effectively manage your sensitivities. With continuous support and follow-up consultations, we ensure that your treatment plan adapts to your evolving needs, empowering you to take control of your allergy management.
Explore Skin Tests: Methodology and Effectiveness
Allergy testing for adults, particularly skin prick tests, involves applying a small amount of allergen to the skin's surface and then piercing it to assess allergic reactions. This method is efficient, typically yielding results within 15 to 20 minutes, which makes it a preferred option among allergists. Skin prick tests are noted for their high sensitivity, with combined sensitivity estimates reaching up to 88.4% for identifying allergic rhinitis. They can detect a broad spectrum of allergens, including pollen, pet dander, and certain foods.
However, this testing method may not be appropriate for individuals with specific medical conditions or those on medications that could affect the results. Recent advancements in evaluation techniques have further enhanced the accuracy of allergy testing for adults, ensuring it remains a cost-effective choice for timely feedback in hypersensitivity diagnosis. For instance, a recent trial demonstrated a 44% reduction in prick reactivity among participants with cat sensitivities, underscoring the effectiveness of this testing approach.
Overall, dermatological assessments are crucial in managing sensitivities, providing immediate information that aids in developing tailored treatment strategies.
Examine Blood Tests: Process and Insights
Allergy assessments, particularly the specific IgE examination, involve collecting a small sample for laboratory analysis to measure IgE antibody levels associated with various allergens. Typically, results take a few days to process, with timelines ranging from 1 to 3 days depending on the laboratory. These assessments are especially beneficial for individuals with dermatological issues, those taking antihistamines, or when cutaneous evaluation is not feasible.
While serum examinations may exhibit reduced sensitivity compared to skin assessments, they provide crucial information regarding potential allergens, including common environmental factors such as dust mites and mold, which significantly contribute to allergic reactions. For instance, a recent study indicated that serum sensitivity evaluations show rates between 70% and 90%, with specificity levels varying from 40% to 100%. This variability highlights the necessity of interpreting results in conjunction with clinical history.
Moreover, patients are advised to refrain from antihistamines for 3-7 days and caffeine for 24 hours prior to testing to ensure accurate results. Although blood tests are generally regarded as less invasive, some patients may experience mild discomfort during the blood draw. Understanding these nuances, along with the impact of environmental allergens, can greatly assist in formulating tailored treatment plans that incorporate allergy testing for adults for effective allergy management.
Pros of Blood Tests:
- Convenient for patients on antihistamines or those with skin conditions.
- No need to discontinue medications prior to testing.
- Provides valuable insights into potential allergens, including dust mites and mold.
Cons of Blood Tests:
- Generally lower sensitivity compared to skin tests.
- Results may require more time to process compared to dermal evaluations.
- Potential for mild discomfort during the extraction.
Compare Skin Tests and Blood Tests: Key Differences and Considerations
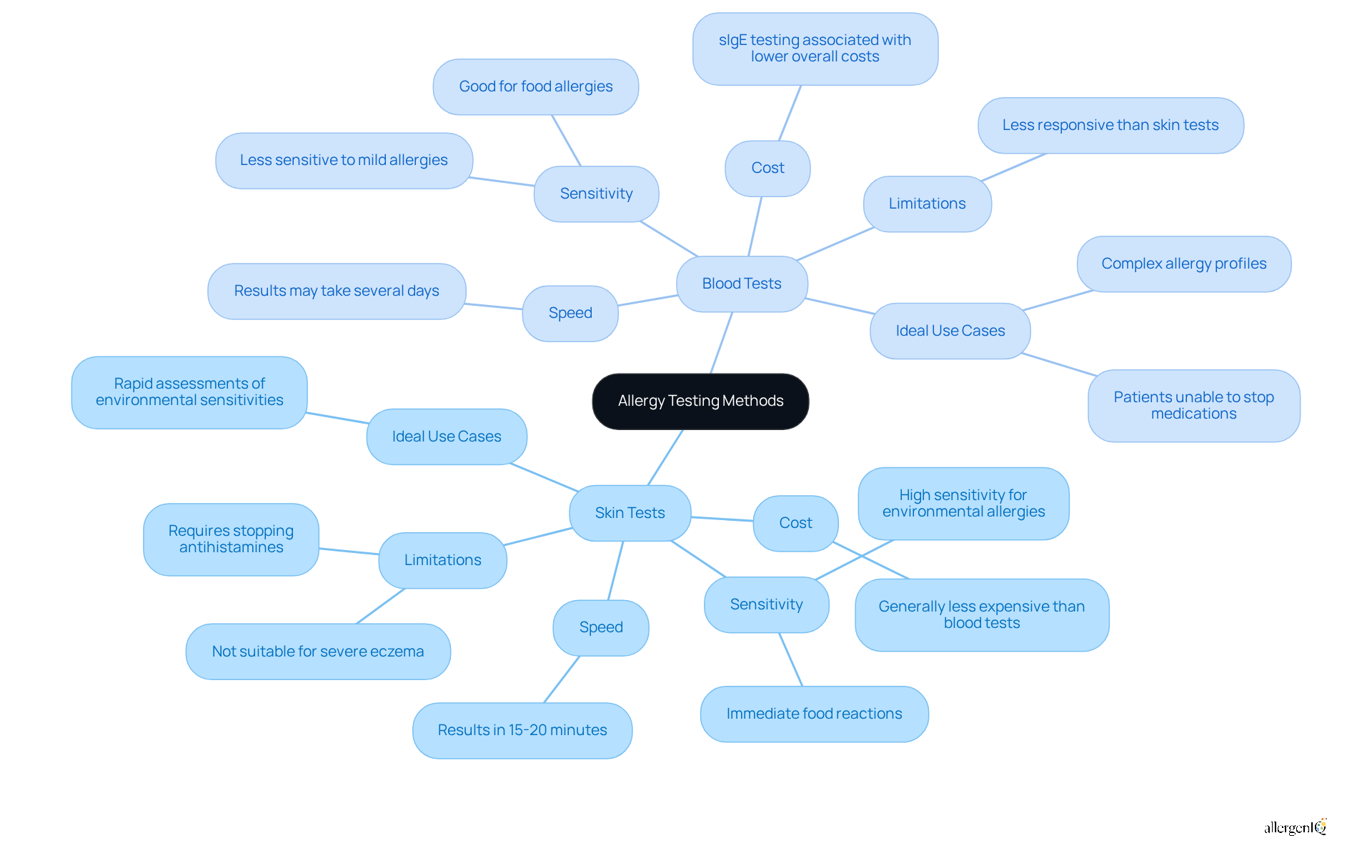
When contrasting skin examinations and blood analyses for sensitivity diagnosis, several key differences emerge. Skin evaluations are generally quicker, yielding results in 15 to 20 minutes, and are often more economical. They exhibit high sensitivity, capable of detecting a wide array of allergens, making them particularly useful for environmental allergies and immediate food reactions. However, patients must refrain from antihistamines prior to evaluation, and these assessments may not be suitable for individuals with severe eczema or sensitive skin.
Conversely, blood analyses, while typically less responsive, provide a safer alternative for individuals unable to undergo dermal evaluations due to skin conditions or medications that may influence results. Blood examinations require only one sample to assess multiple allergens, making them ideal for individuals with complex allergy profiles or those who may find skin prick tests challenging.
Cost considerations significantly influence the decision-making process. Research indicates that sIgE assessment, a specific type of blood analysis, is associated with reduced overall expenses and fewer specialist appointments compared to traditional skin prick tests. For instance, patients undergoing sIgE assessments averaged 1.8 fewer visits to allergists than those who solely had skin prick tests.
Real-world examples effectively illustrate these differences. For individuals with moderate to severe sensitivities, blood examinations can be particularly advantageous, allowing for comprehensive assessments without the need to discontinue antihistamines. In contrast, skin evaluations are often preferred for rapid assessments of environmental sensitivities, especially in scenarios where prompt results are critical.
Ultimately, the choice between skin and blood tests should be guided by individual health conditions, preferences, and the recommendations of a healthcare provider, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate and effective allergy diagnosis.
Conclusion
Allergy testing for adults plays a crucial role in identifying allergens that can provoke adverse reactions. The two primary methods - skin tests and blood tests - each present distinct advantages and considerations. This allows healthcare providers to customize treatment plans to meet individual needs. Skin tests are known for their rapid results and high sensitivity, while blood tests offer a less invasive alternative for patients who may not tolerate dermal evaluations.
The effectiveness of skin prick tests is noteworthy, as they provide quick turnaround times and can detect a broad spectrum of allergens. In contrast, blood tests are particularly advantageous for patients with specific medical conditions or those on medications that complicate skin testing. Both methods are integral to effective allergy management, ensuring that patients receive accurate diagnoses and appropriate treatment strategies.
Ultimately, the decision between skin and blood tests should be guided by personal health circumstances and professional advice. As allergy testing continues to advance, understanding these methods empowers individuals to take control of their health and manage their allergies more effectively. Selecting the appropriate testing method is a vital step toward enhancing quality of life, enabling individuals to navigate their sensitivities with confidence and clarity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of allergy testing for adults?
Allergy testing for adults is crucial for identifying allergens that provoke adverse reactions in individuals, allowing healthcare providers to recommend tailored treatment plans.
What are the two primary methods of allergy testing?
The two primary methods for evaluating sensitivity are dermal examinations (skin evaluations) and serum examinations (blood analyses).
How do skin evaluations work?
Skin evaluations involve exposing the skin to small quantities of allergens through pricks or scratches to assess sensitivity.
What do blood analyses assess in allergy testing?
Blood analyses assess the immune system's response to allergens by detecting specific IgE antibodies in the bloodstream.
How does AllergenIQ enhance the allergy testing process?
AllergenIQ offers innovative at-home sensitivity testing that matches the accuracy of in-clinic evaluations, allowing individuals to perform tests conveniently from home.
What happens after an individual completes the at-home allergy test with AllergenIQ?
After completing the test, individuals receive personalized consultations with specialists who review their responses and symptoms to formulate customized treatment strategies.
How does AllergenIQ support individuals in managing their allergies?
AllergenIQ provides continuous support and follow-up consultations to ensure that the treatment plan adapts to evolving needs, empowering individuals to take control of their allergy management.




