Introduction
Mold allergies in workplace environments present a significant challenge to both employee health and organizational productivity. Understanding the causes and symptoms of these allergies is essential, as they can result in increased absenteeism and substantial healthcare costs.
To foster a healthier work environment, effective management strategies are crucial; however, many employers find it difficult to implement comprehensive approaches. Thus, organizations face the pressing question: how can they balance the need for a productive workspace with the imperative of safeguarding employee well-being against these hidden allergens?
Understand Mold Allergies: Causes and Symptoms
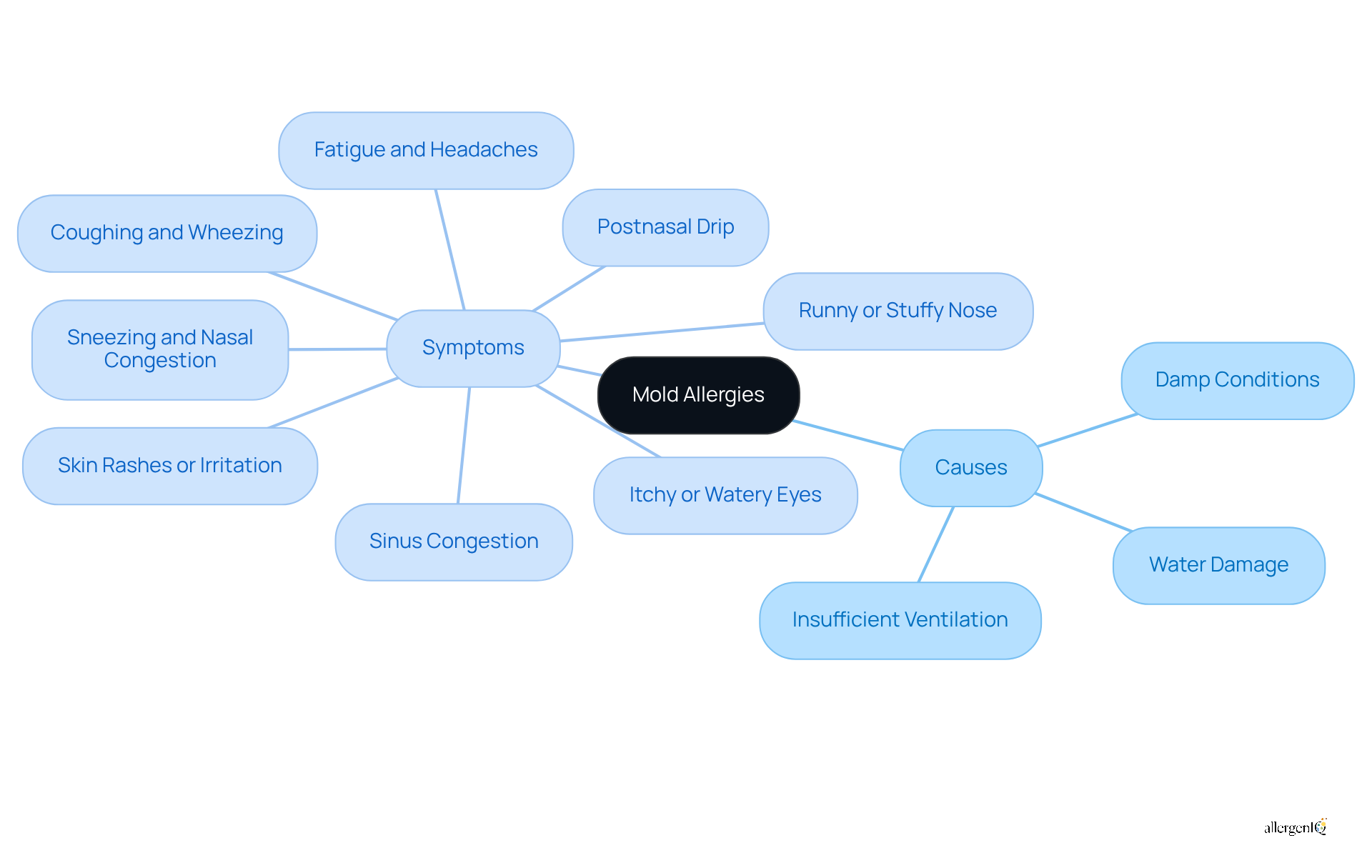
Fungal sensitivities arise from the immune system's response to spore particles, which are minute fungi prevalent in both indoor and outdoor environments. These sensitivities are frequently triggered by damp conditions, water damage, and insufficient ventilation. Symptoms can vary widely among individuals, but they typically include:
- Sneezing and nasal congestion
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Coughing and wheezing
- Skin rashes or irritation
- Fatigue and headaches
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Postnasal drip
- Sinus congestion
Recognizing these symptoms early is essential for timely intervention and treatment, significantly enhancing employee well-being and productivity. Research indicates that allergic rhinitis, often exacerbated by exposure to fungi, leads to an average of 3.6 missed workdays annually. This statistic underscores the importance of effective management strategies in the workplace. Furthermore, health issues related to fungi contribute to approximately $19 billion in healthcare costs each year, highlighting the financial impact of fungal sensitivities on businesses. By addressing fungal sensitivities proactively, employers can foster a healthier work environment and mitigate productivity losses. Additionally, it is crucial to consider dust mites, which are common irritants that can also provoke similar symptoms, complicating the management of sensitivities.
Diagnose Mold Allergies: Best Practices for Accurate Identification
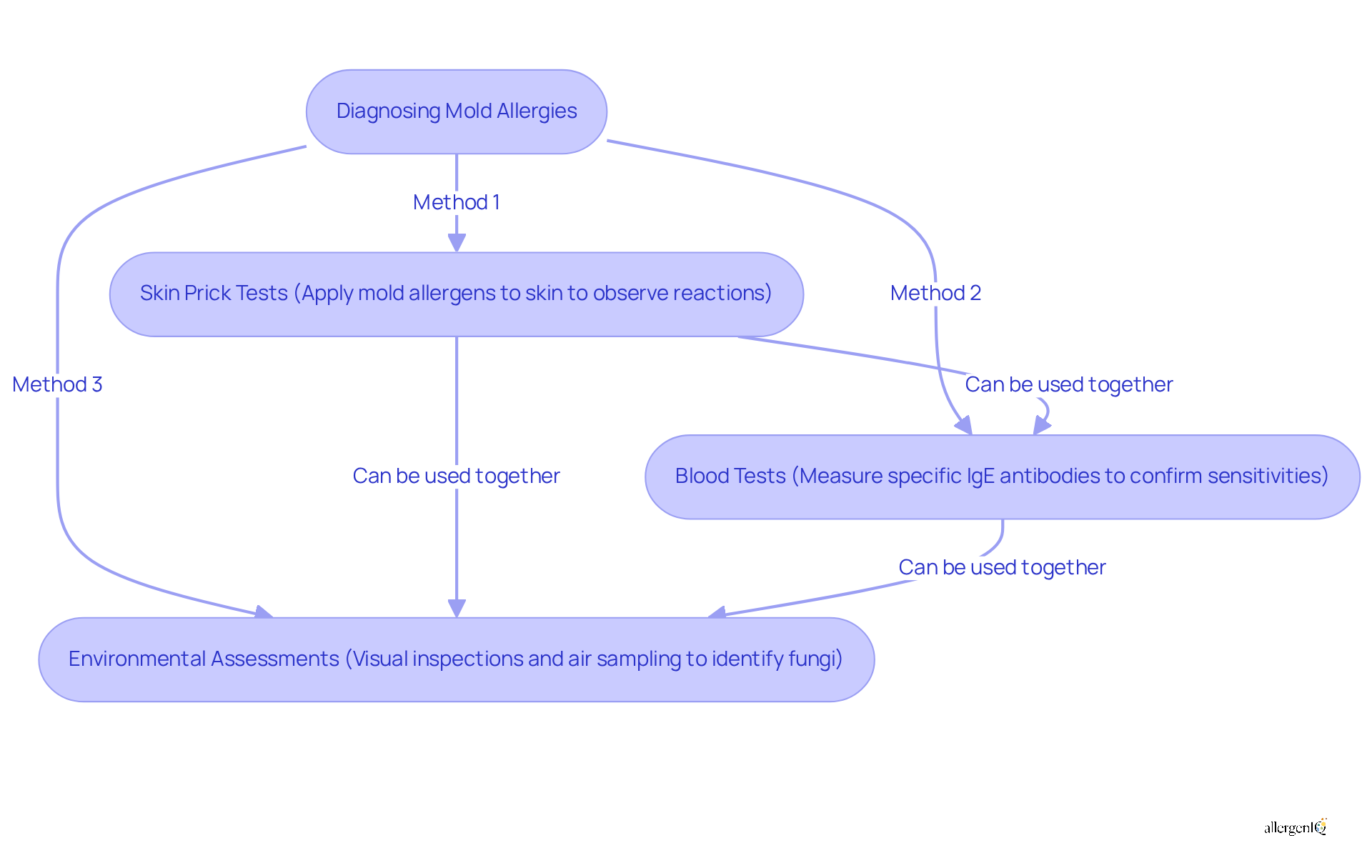
Accurate diagnosis of fungal allergies requires a multifaceted approach that combines thorough evaluations of medical history, physical assessments, and targeted allergy tests. The primary diagnostic methods include:
- Skin Prick Tests: This technique involves applying small quantities of mold allergens to the skin to observe any allergic reactions, offering immediate insights into sensitivities.
- Blood Tests: These tests measure specific IgE antibodies, confirming sensitivities to fungi and serving as a reliable alternative when skin tests are impractical.
- Environmental Assessments: Conducting visual inspections and air sampling in the environment helps identify the presence of fungi, providing essential context for understanding symptoms.
Employers play a crucial role in fostering health by encouraging employees to pursue medical evaluations if they suspect sensitivities to fungi. This proactive strategy enables timely diagnosis and effective mold allergy treatment, ultimately enhancing workplace well-being.
Implement Treatment Strategies: Effective Approaches for Relief
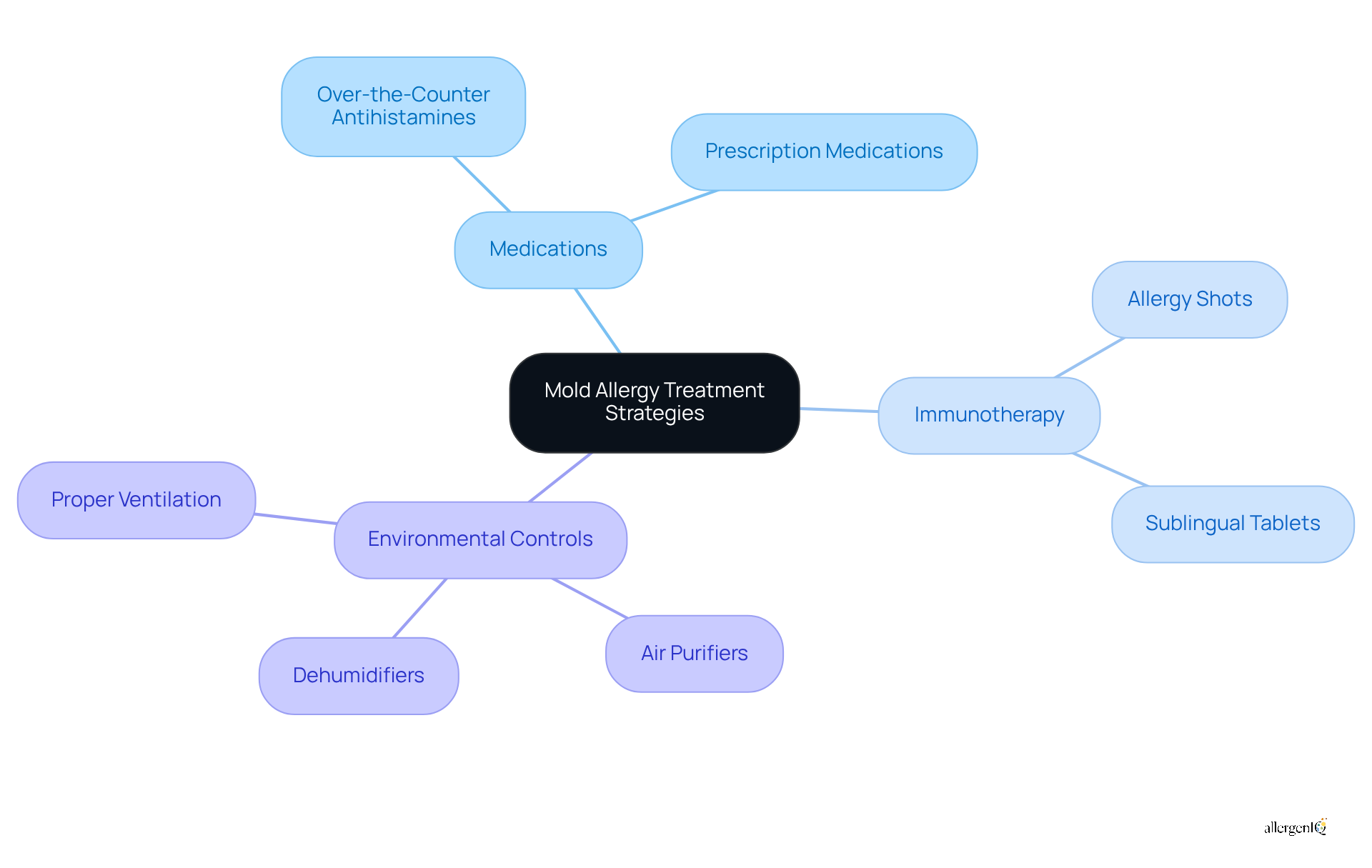
Effective treatment strategies for mold allergies encompass several key approaches:
-
Medications: Over-the-counter antihistamines and nasal corticosteroids are effective in alleviating symptoms. In cases of severe allergies, prescription medications may be required to provide adequate relief.
-
Immunotherapy: As a mold allergy treatment, this includes allergy shots or sublingual tablets that gradually desensitize the immune system to fungal allergens, offering a long-term solution for affected individuals.
-
Environmental Controls: Implementing measures such as air purifiers, dehumidifiers, and ensuring proper ventilation can significantly mitigate fungal exposure in the workplace.
Furthermore, recognizing the impact of dust mites as a prevalent allergen can enhance management strategies. Dust mites thrive in domestic dust and can exacerbate symptoms related to fungal sensitivities. It is essential for employers to collaborate with healthcare providers to develop comprehensive mold allergy treatment plans tailored to the specific needs of each employee, considering both fungal and dust mite sensitivities. This holistic approach is vital for effective allergy management, particularly in environments where allergens are prevalent.
Prevent Mold Exposure: Practical Tips for a Healthier Environment
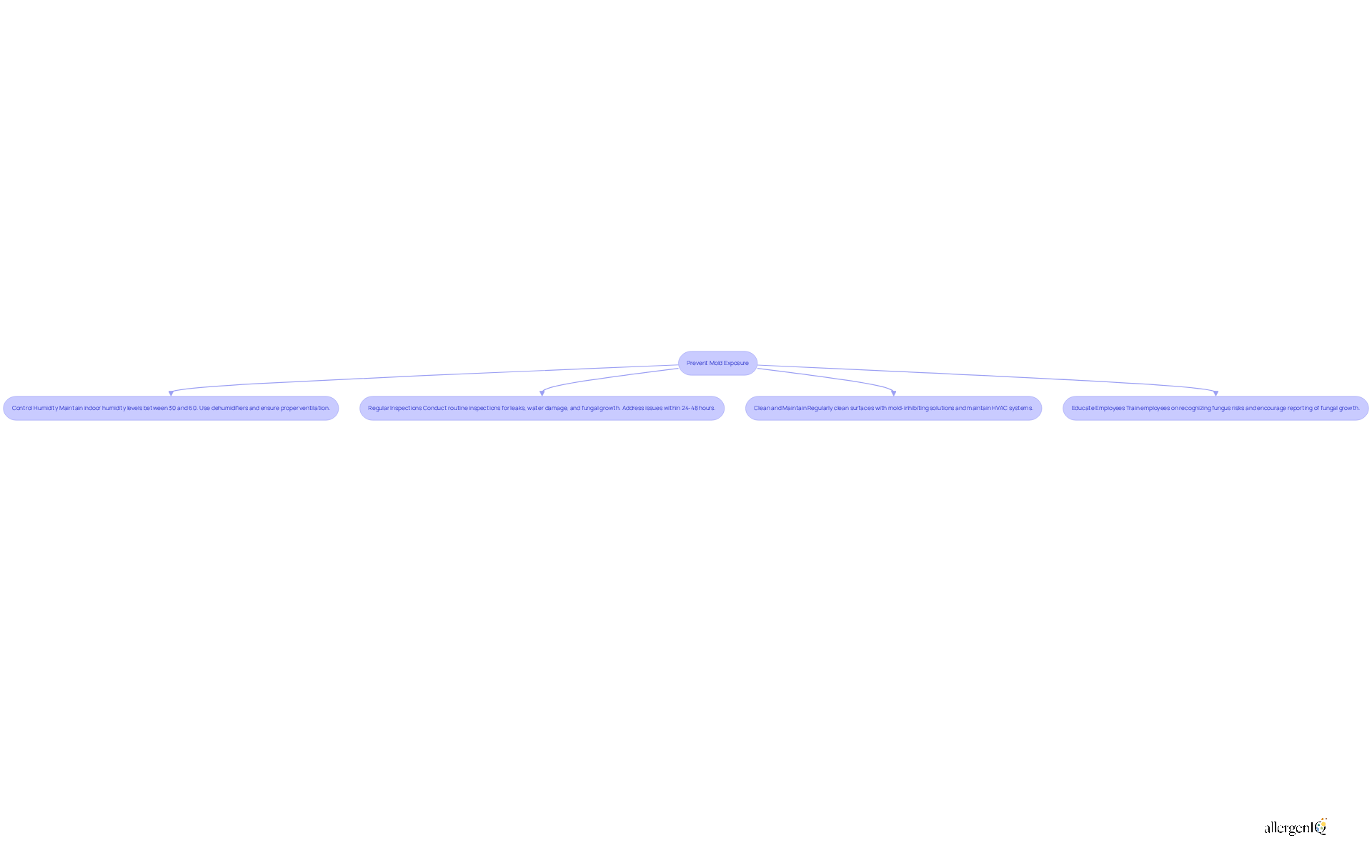
To effectively prevent mold exposure in the workplace, it is essential to implement the following strategies:
-
Control Humidity: Maintaining indoor humidity levels between 30% and 60% is crucial. Utilize dehumidifiers and ensure proper ventilation. High humidity can lead to fungal growth; research indicates that damp conditions can contribute to a 30-50% increase in respiratory illnesses.
-
Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections for leaks, water damage, and fungal growth. Swiftly addressing these issues is vital; specialists recommend responding to signs of water intrusion within 24 to 48 hours to inhibit fungal development.
-
Clean and Maintain: Regularly clean surfaces with mold-inhibiting solutions and ensure that HVAC systems are properly maintained. Adequate airflow is critical in areas prone to moisture, as stagnant air can exacerbate fungal issues.
-
Educate Employees: Provide training to employees on recognizing fungus risks and encourage them to report any signs of fungal growth. Empowering employees with knowledge fosters a proactive culture regarding fungus management.
Implementing these preventive measures not only cultivates a healthier work environment but also significantly reduces the incidence of mold allergy treatment needs among employees, ultimately enhancing overall workplace productivity.
Conclusion
Addressing mold allergies in the workplace is essential for cultivating a healthy and productive environment. By comprehending the causes and symptoms of mold allergies, employers can implement significant measures to mitigate their effects on employees. This proactive strategy not only enhances employee well-being but also alleviates the financial burden associated with healthcare costs and lost productivity.
The article delineates crucial best practices for effectively diagnosing and treating mold allergies. Key strategies encompass:
- Accurate identification through medical evaluations
- The implementation of effective treatment options such as medications and immunotherapy
- The adoption of preventive measures to minimize mold exposure
Regular inspections, humidity control, and employee education are vital components in establishing a safer workplace, ultimately leading to a decrease in allergy-related issues.
In conclusion, prioritizing mold allergy management transcends mere health concerns; it represents a strategic business decision that can enhance employee satisfaction and productivity. By embracing these best practices, employers can foster a healthier workspace that benefits all stakeholders. Taking decisive action now can yield lasting improvements in workplace health and efficiency, underscoring the necessity for organizations to integrate these strategies into their commitment to employee well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes mold allergies?
Mold allergies are caused by the immune system's response to spore particles from fungi, which are commonly found in both indoor and outdoor environments. These sensitivities are often triggered by damp conditions, water damage, and insufficient ventilation.
What are the common symptoms of mold allergies?
Common symptoms of mold allergies include sneezing and nasal congestion, itchy or watery eyes, coughing and wheezing, skin rashes or irritation, fatigue and headaches, runny or stuffy nose, postnasal drip, and sinus congestion.
Why is it important to recognize mold allergy symptoms early?
Recognizing mold allergy symptoms early is essential for timely intervention and treatment, which can significantly enhance employee well-being and productivity.
How do mold allergies affect workplace productivity?
Research indicates that allergic rhinitis, often exacerbated by exposure to fungi, leads to an average of 3.6 missed workdays annually, highlighting the importance of effective management strategies in the workplace.
What is the financial impact of fungal sensitivities on businesses?
Health issues related to fungi contribute to approximately $19 billion in healthcare costs each year, underscoring the financial impact of fungal sensitivities on businesses.
How can employers address fungal sensitivities in the workplace?
Employers can foster a healthier work environment and mitigate productivity losses by addressing fungal sensitivities proactively.
What other irritants should be considered alongside mold allergies?
It is crucial to consider dust mites, which are common irritants that can provoke similar symptoms, complicating the management of sensitivities.




