Introduction
Navigating the complexities of a casein protein allergy can be daunting, especially considering the widespread presence of dairy in many diets. Approximately 2-5% of infants worldwide are affected by this condition, making it essential to understand effective management strategies to ensure health and well-being. Families can employ various strategies to avoid exposure and alleviate symptoms while maintaining a balanced diet. This guide outlines five essential steps that empower individuals to take control of their dietary choices and enhance their quality of life in the face of the challenges posed by casein protein allergies.
Understand Casein Protein Allergy
A milk protein allergy arises when the immune system erroneously identifies milk proteins, commonly found in dairy products, as harmful. This misidentification can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild reactions such as hives and gastrointestinal discomfort to severe responses like anaphylaxis. It is crucial to recognize that one of the two primary proteins in cow's milk, alongside whey, plays a significant role in identifying potential sources of exposure. Individuals with this sensitivity must exercise caution, as specific proteins can be hidden in numerous processed foods and dairy items.
Recent studies indicate that approximately 2-5% of infants globally are affected by cow's milk protein sensitivity, with one protein being a major contributor. Data from 2025 reveal that non-Hispanic black and non-Hispanic white children show higher sensitization rates to milk, underscoring the need for targeted awareness and intervention strategies. Experts in allergens emphasize the importance of comprehensive education for families managing a casein protein allergy, as understanding the nuances of casein can significantly improve dietary choices and reduce the risk of unintentional exposure.
Real-world examples demonstrate that families often face intricate dietary restrictions, necessitating careful label reading and effective communication with food providers to ensure safety. The latest research highlights the critical nature of early diagnosis and intervention, as timely treatment can prevent the progression of allergic conditions and enhance the quality of life for those affected. Additionally, it is noteworthy that around 60% of individuals with cow's milk sensitivity have the IgE-mediated type, which can influence the severity of symptoms and treatment strategies.
The economic implications associated with casein protein allergy management are substantial, particularly for low-income families, who may face significant out-of-pocket expenses for hypoallergenic formulas and related healthcare costs. At AllergenIQ, we provide tailored management solutions for sensitivities, including precise testing and personalized treatment plans, all delivered virtually through an efficient online consultation process. This approach ensures that families receive the expert support they require. A coordinated strategy involving diverse teams is essential for providing comprehensive care and assistance to families dealing with this condition.
Identify Symptoms of Casein Allergy
Symptoms of a casein protein allergy can manifest in various ways, impacting different systems within the body. Common symptoms include skin reactions, gastrointestinal issues, respiratory problems, and, in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
-
Skin Reactions: Individuals may experience hives, rashes, or eczema, often as immediate responses to dairy consumption. These skin reactions can be particularly distressing for children, impacting their comfort and quality of life.
-
Gastrointestinal Issues: Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain can occur shortly after ingesting dairy products. These gastrointestinal disturbances are frequently reported in children, highlighting the need for careful dietary management.
-
Respiratory Problems: Wheezing, coughing, nasal congestion, or difficulty breathing may arise, indicating a more severe allergic response. These respiratory issues can escalate quickly, necessitating prompt attention.
-
Anaphylaxis: In severe instances, indicators can advance to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening reaction that necessitates urgent medical assistance. Anaphylaxis can manifest with signs such as shortness of breath, constriction of the throat, and a rapid, weak pulse. The occurrence of anaphylaxis in milk protein sensitivities underscores the vital significance of promptly identifying signs of a casein protein allergy.
Current medical views stress the importance of attentiveness in recognizing reactions to proteins, particularly casein protein allergy, especially in children, as early detection can greatly enhance treatment outcomes. Real-world examples illustrate the urgency of this issue; for instance, a tragic case highlighted the consequences of delayed recognition and treatment of an allergic reaction in a school setting. Understanding these signs is essential for effective management and prompt care, ensuring that individuals with protein sensitivities can navigate their dietary limitations safely.
Get Diagnosed for Casein Allergy
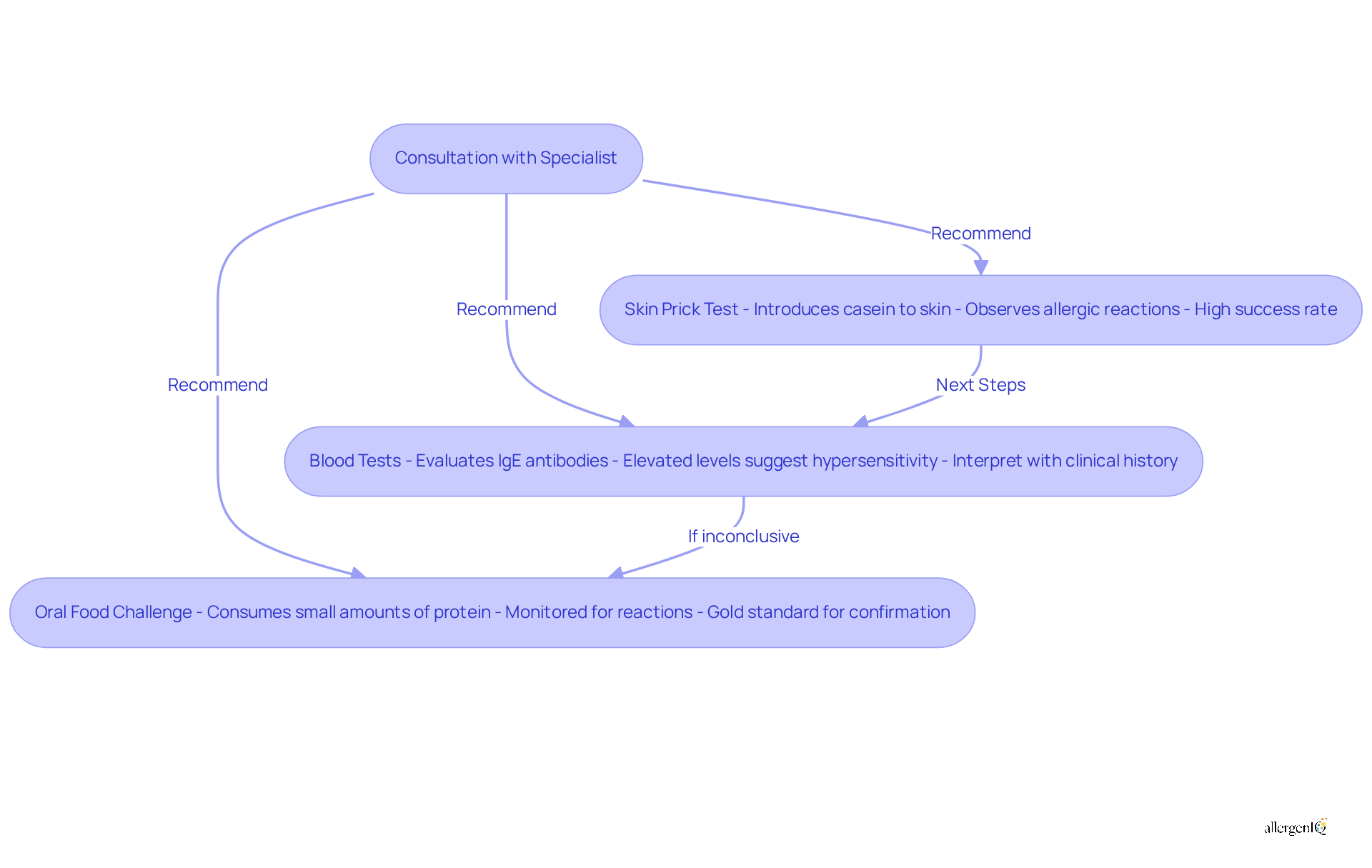
Identifying a protein sensitivity requires consultation with a specialist, who may recommend several essential tests to ensure accurate detection of the condition. These tests include:
- Skin Prick Test: This test involves introducing a small amount of casein to the skin and observing for allergic reactions. Research indicates that skin prick tests have a high success rate in diagnosing milk protein sensitivities, establishing them as a reliable initial step in the diagnostic process.
- Blood Tests: These tests evaluate the presence of IgE antibodies specific to milk protein. Elevated IgE levels may suggest hypersensitivity; however, results should be interpreted in conjunction with clinical history and symptoms.
- Oral Food Challenge: Conducted under medical supervision, this test entails consuming small amounts of a specific protein to monitor for reactions. It is considered the gold standard for confirming a sensitivity to milk protein, particularly when other tests yield inconclusive results.
Accurate diagnosis is vital for effective management and treatment planning. Allergists emphasize that understanding specific triggers and reactions can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with a casein protein allergy. For instance, a retrospective study of pediatric patients revealed that those who underwent comprehensive testing, including skin prick tests and oral food challenges, experienced better outcomes in managing their conditions. As of 2025, advancements in sensitivity testing continue to enhance diagnostic accuracy, ensuring that individuals receive tailored care that addresses their unique needs.
Avoid Casein in Your Diet
To effectively manage a protein allergy, individuals must strictly avoid all sources of that protein. Here are actionable steps:
-
Read Labels: Always scrutinize ingredient lists for casein or caseinate, as these can be hidden in many processed foods. Research indicates that approximately 20-30% of processed foods include protein, making label reading essential for safety. Nutritionists recommend checking for phrases like 'contains milk ingredients' or 'made with milk ingredients' on food labels to avoid accidental exposure.
-
Choose Alternatives: Opt for non-dairy substitutes such as almond milk, soy milk, or oat milk, which are naturally free from dairy proteins. Many individuals have successfully transitioned to these options, finding them both satisfying and safe.
-
Educate Yourself: Familiarize yourself with foods that are important to avoid if you have a casein protein allergy, including cheese, yogurt, and certain baked goods. Understanding these sources is essential for making informed dietary choices and avoiding allergic reactions, particularly those caused by casein protein allergy. Nutritionists stress the significance of being proactive in dietary oversight, advising individuals to always check for concealed dairy components in packaged foods.
-
Real-Life Examples: Numerous families have effectively managed sensitivities to milk proteins by adopting plant-based diets, utilizing resources such as vegan cheese substitutes created from nuts or soy. These options not only provide variety but also help maintain nutritional balance.
-
Casein Protein Allergy Diet Tips: In 2025, it is recommended to explore a variety of casein-free products suitable for individuals with a casein protein allergy available in stores, including snacks and dairy substitutes like cashew-based cheeses and coconut yogurt. Engaging with community forums or support groups, such as those found on platforms like Facebook or Reddit, can also provide valuable insights and shared experiences, enhancing dietary management strategies.
Explore Treatment Options for Casein Allergy
While strict avoidance of casein is the cornerstone of managing a casein protein allergy, several additional treatment options can enhance safety and quality of life.
-
Antihistamines are effective in alleviating mild allergic symptoms such as hives, itching, and nasal congestion. Allergists often recommend these medications as a first-line response to manage such symptoms, providing immediate relief for patients experiencing mild reactions.
-
Epinephrine Auto-Injectors are crucial for individuals at risk of severe allergic reactions. Recent data indicates that prescriptions for epinephrine auto-injectors have become increasingly common among patients with food sensitivities, including milk protein. This trend underscores the importance of preparedness in case of accidental exposure.
-
Oral Immunotherapy (OIT) is an innovative method gaining traction as a potential remedy for food sensitivities, including milk protein. OIT involves the gradual introduction of small amounts of casein under strict medical supervision, aiming to build tolerance for those with a casein protein allergy over time. As new treatments continue to advance in 2025, OIT symbolizes a promising path for individuals seeking to manage their sensitivities more effectively. Consulting with an allergist is essential to create a tailored strategy that considers individual health needs and risk factors.
Incorporating these strategies can significantly improve the management of casein protein allergy, allowing individuals to navigate their dietary restrictions with greater confidence and safety.
Conclusion
Effectively managing a casein protein allergy necessitates a thorough understanding of the condition and the implementation of proactive measures to ensure safety and well-being. Recognizing symptoms, obtaining an accurate diagnosis, and adhering to strict dietary restrictions are essential steps that individuals can take to significantly mitigate the risk of allergic reactions. Education and awareness play a pivotal role, as informed choices are critical for navigating the complexities associated with this allergy.
Key insights emphasize the importance of:
- Meticulous label reading
- Exploring non-dairy alternatives
- Considering various treatment options
Strategies such as:
- Antihistamines for mild symptoms
- Epinephrine auto-injectors for severe reactions
are vital components of effective management. Additionally, advancements in oral immunotherapy offer promising avenues for individuals seeking to develop tolerance over time.
Ultimately, the successful management of a casein protein allergy relies on a coordinated approach that integrates dietary vigilance, medical guidance, and community support. Individuals and families are encouraged to engage with available resources and support networks to share experiences and strategies. By remaining proactive and well-informed, those affected can confidently navigate their dietary limitations, thereby enhancing their quality of life and minimizing the risk of severe allergic responses.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a casein protein allergy?
A casein protein allergy occurs when the immune system mistakenly identifies casein, a protein found in cow's milk, as harmful, leading to various symptoms ranging from mild reactions to severe responses like anaphylaxis.
What are the common symptoms of a casein protein allergy?
Common symptoms include skin reactions (hives, rashes, eczema), gastrointestinal issues (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain), respiratory problems (wheezing, coughing, nasal congestion), and in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
How prevalent is cow's milk protein sensitivity among infants?
Approximately 2-5% of infants globally are affected by cow's milk protein sensitivity, with specific proteins, including casein, being major contributors.
Which demographics show higher sensitization rates to milk?
Data from 2025 indicate that non-Hispanic black and non-Hispanic white children show higher sensitization rates to milk.
Why is education important for families managing a casein protein allergy?
Comprehensive education helps families understand the nuances of casein, improving dietary choices and reducing the risk of unintentional exposure to allergens.
What are the economic implications of managing a casein protein allergy?
Managing a casein protein allergy can lead to significant out-of-pocket expenses for hypoallergenic formulas and healthcare costs, particularly impacting low-income families.
How can families receive support for managing casein protein allergies?
Families can access tailored management solutions, including precise testing and personalized treatment plans, through virtual consultations provided by organizations like AllergenIQ.
What is anaphylaxis and how is it related to casein protein allergy?
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening allergic reaction that can occur in severe cases of casein protein allergy, characterized by symptoms such as shortness of breath, throat constriction, and a rapid, weak pulse, requiring urgent medical assistance.
What role does early diagnosis and intervention play in managing casein protein allergies?
Early diagnosis and intervention are critical as they can prevent the progression of allergic conditions and enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.




