Introduction
Understanding antibiotic allergies is essential in the current healthcare landscape, where misdiagnosis can result in unnecessary treatment complications and increased costs. This article explores the complexities of antibiotic allergy management, providing insights into:
- Symptoms
- Diagnostic methods
- Effective treatment strategies
Notably, a significant percentage of patients are misclassified as allergic. Therefore, how can healthcare professionals ensure accurate evaluations and optimize patient care?
Define Antibiotic Allergies and Their Impact
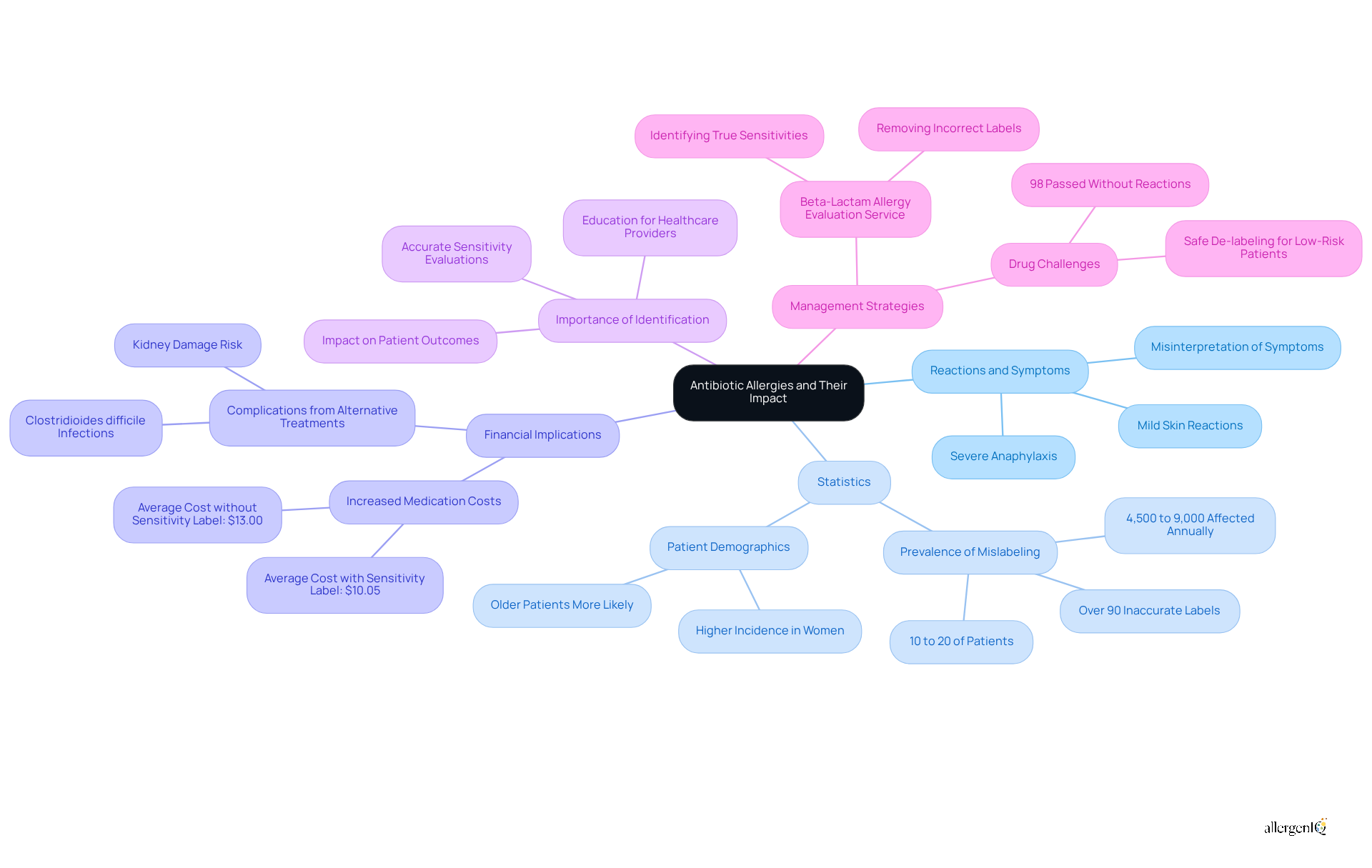
Reactions to medications represent negative immune responses triggered by these drugs, with symptoms ranging from mild skin reactions to severe anaphylaxis. Such sensitivities pose significant challenges in healthcare, often leading to the unnecessary avoidance of effective medications, which can result in increased medical costs and prolonged illness. Current statistics indicate that approximately 10% to 20% of hospitalized patients are labeled as allergic to beta-lactam medications, with over 90% of these classifications being inaccurate. This mislabeling potentially affects between 4,500 and 9,000 patients annually at institutions like Michigan Medicine, highlighting the urgent need for accurate sensitivity evaluations.
The financial implications of medication sensitivities are considerable. Patients identified with a penicillin sensitivity incur higher medication costs, averaging $10.05 compared to $13.00 for those without such labels. Moreover, the avoidance of beta-lactam medications, often the most effective treatment options, can lead to the prescription of less effective alternatives, increasing the risk of complications such as kidney damage and Clostridioides difficile infections.
Healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of identifying antibiotic sensitivities for effective antibiotic allergy treatment to improve patient outcomes. A systematic approach to evaluating and correcting incorrect sensitivity labels can significantly enhance infection management and improve antibiotic allergy treatment, ultimately reducing healthcare expenses. Research indicates that 98% of patients who underwent drug challenges for beta-lactam sensitivities did so without adverse reactions, underscoring the potential for safe de-labeling.
Real-world examples illustrate the success of medication sensitivity management strategies. The Beta-Lactam Allergy Evaluation Service, for instance, has effectively identified true sensitivities while removing labels from individuals who are not sensitive, thereby improving treatment options for thousands. This initiative not only streamlines patient care but also enhances medication management, ultimately benefiting both patients and healthcare systems.
Identify Symptoms of Antibiotic Allergies
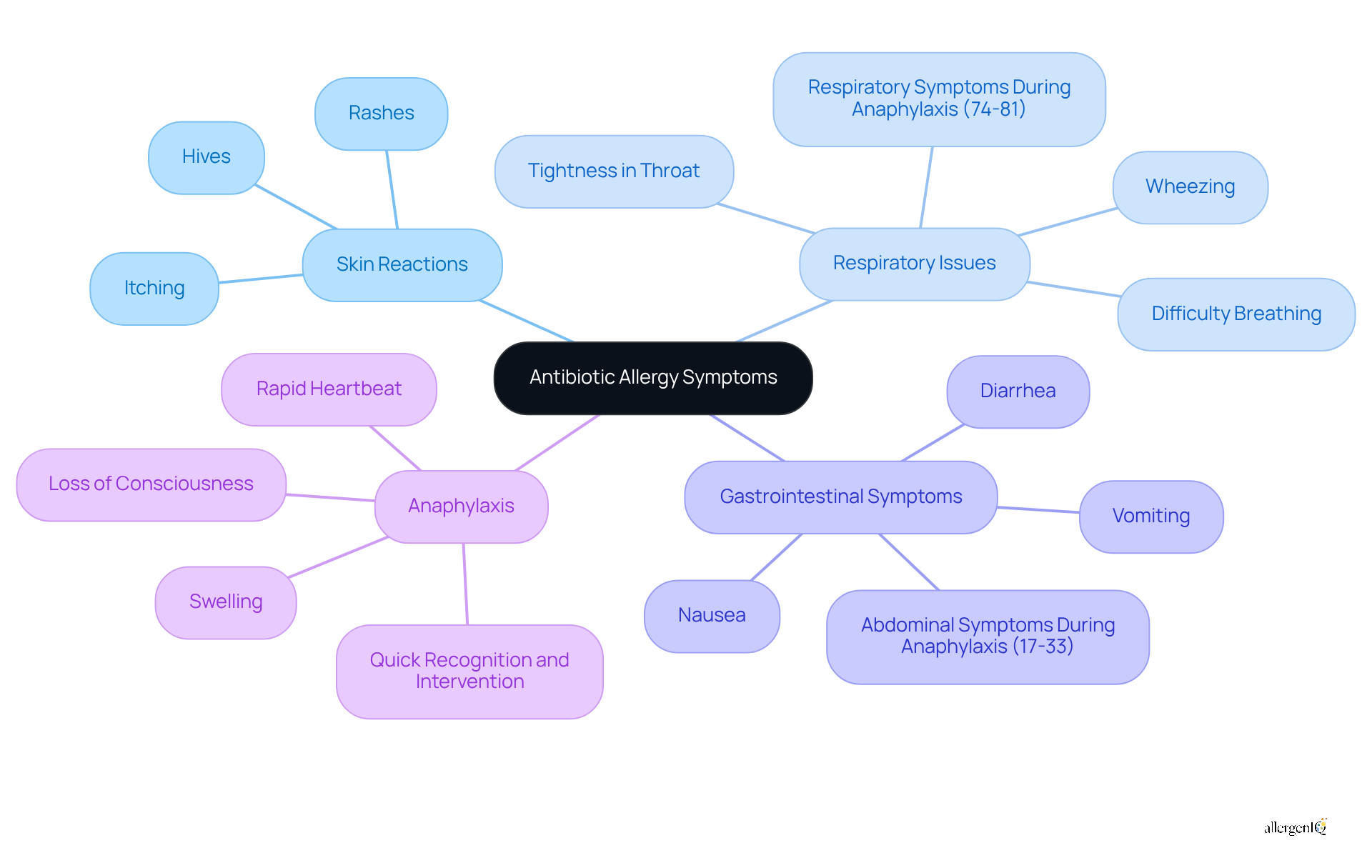
Recognizing the symptoms of antibiotic allergies is crucial for timely intervention and effective antibiotic allergy treatment. Common symptoms include skin reactions, respiratory issues, gastrointestinal symptoms, and anaphylaxis.
-
Skin Reactions: These may manifest as hives, rashes, or itching, affecting a significant portion of individuals experiencing allergic reactions.
-
Respiratory Issues: Symptoms such as wheezing, difficulty breathing, or tightness in the throat can occur. Notably, 74-81% of individuals develop respiratory symptoms during anaphylaxis.
-
Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea are also common, with 17-33% of individuals experiencing abdominal symptoms during anaphylactic episodes.
-
Anaphylaxis: This severe, life-threatening reaction is characterized by symptoms such as swelling, rapid heartbeat, and loss of consciousness. Anaphylaxis can occur within minutes to hours after contact with the allergen, making quick recognition and intervention essential.
Comprehending these symptoms can greatly enhance outcomes, as early identification leads to faster care. For instance, 42% of people seek medical attention within 15 minutes of symptom onset, underscoring the significance of awareness and readiness in managing medication sensitivities.
Explore Diagnostic Methods for Antibiotic Allergies
Diagnostic methods for antibiotic allergies include several key approaches that significantly enhance the accuracy of assessments and treatment decisions.
-
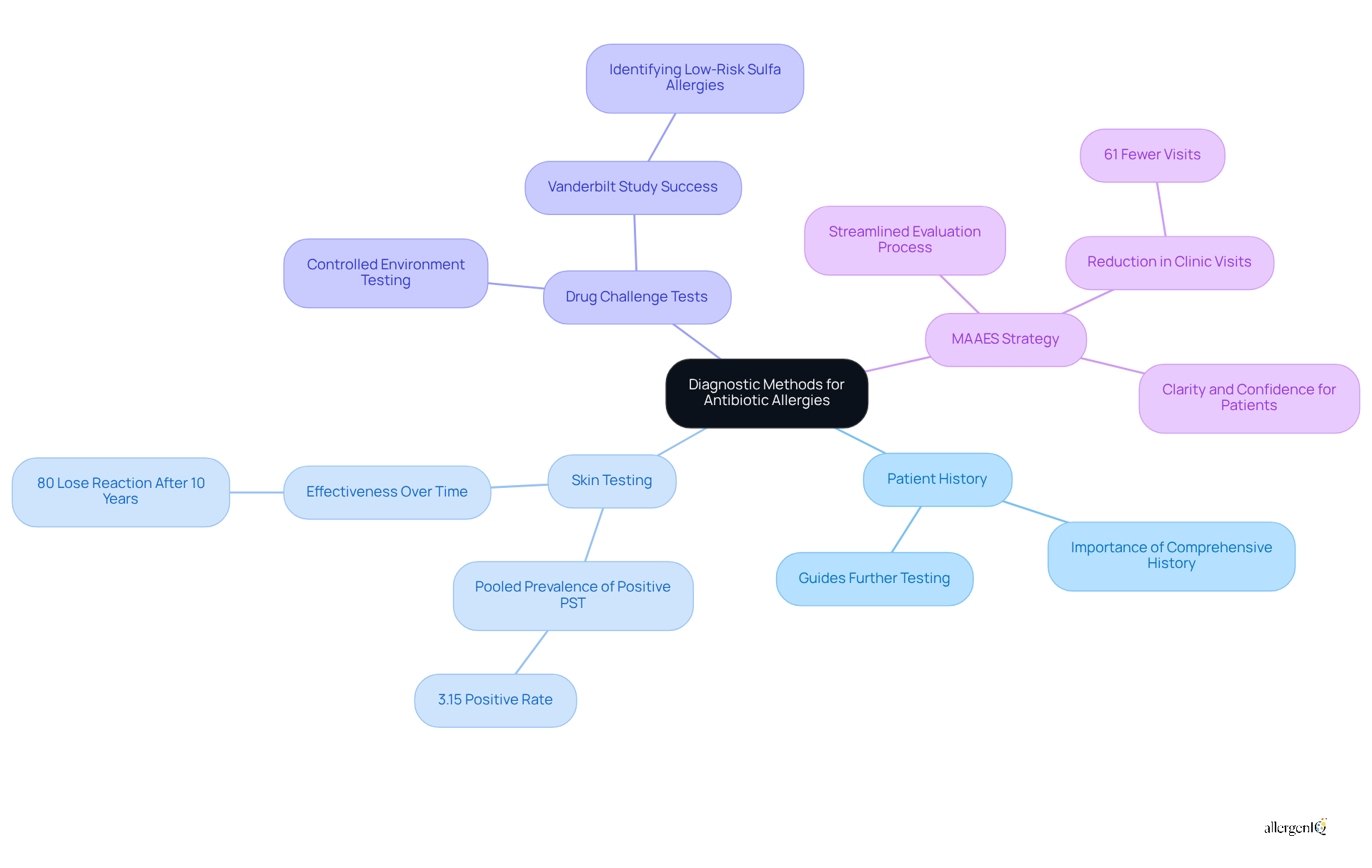
Patient History is fundamental. A comprehensive account of previous reactions to antibiotics is crucial, as it helps clinicians identify patterns and potential risks associated with specific medications. This information guides further testing and management strategies.
-
Skin Testing is another vital method. It involves applying a small amount of the medication to the skin to monitor for any adverse reactions. Recent advancements in skin testing have yielded promising results, with studies indicating a pooled prevalence of positive penicillin skin testing (PST) at 3.15%. This method is particularly effective in recognizing true sensitivities, as approximately 80% of individuals with a genuine penicillin sensitivity may lose that reaction after about ten years.
-
Drug Challenge Tests are conducted in a controlled environment. These assessments involve administering the medication to verify or exclude a hypersensitivity. A study from Vanderbilt demonstrated that physicians could effectively recognize and refute low-risk sulfa drug sensitivities through oral challenges, significantly improving outcomes for individuals, especially in transplant situations.
These diagnostic methods not only assist clinicians in accurately assessing the risk of allergic reactions but also streamline the evaluation process. For instance, the innovative multiple medication sensitivity evaluation strategy (MAAES) has reduced the number of clinic visits by 61%, allowing for the simultaneous assessment of various sensitivities in a single visit. This approach enhances efficiency and provides individuals with clarity and assurance in their care plans.
Review Treatment Options for Antibiotic Allergies
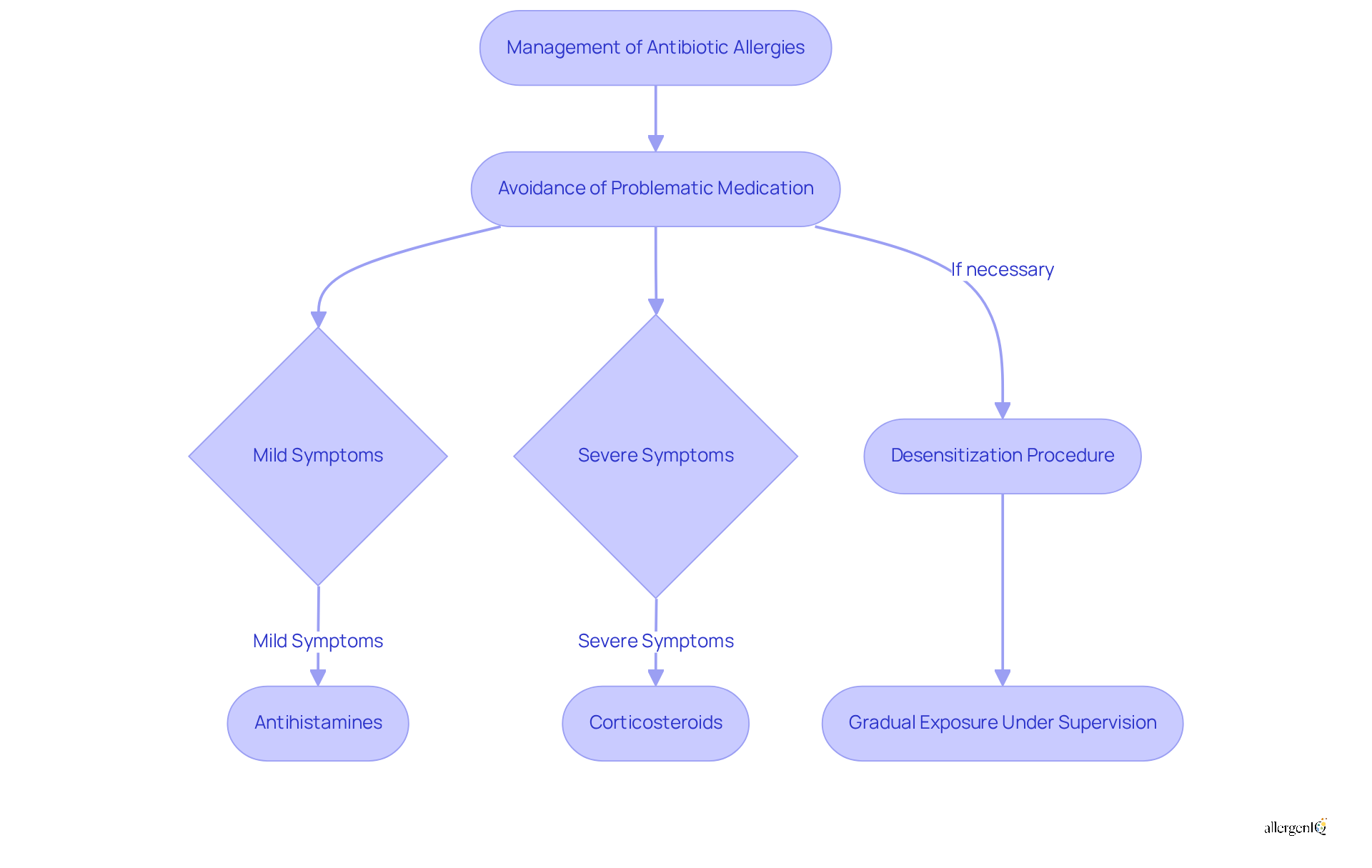
Efficient management of medication sensitivities involves tailored approaches based on the severity of allergic reactions, which may include antibiotic allergy treatment. The primary strategy is avoidance, where individuals steer clear of the problematic medication to avert adverse responses. For mild allergic symptoms, such as itching and hives, antihistamines are typically employed to alleviate discomfort. In instances of more severe reactions, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and effectively manage symptoms.
At AllergenIQ, we prioritize personalized sensitivity management through precise testing, including IgE antibody assessments, and customized treatment plans delivered virtually. This approach allows individuals to receive tailored care from the comfort of their homes, ensuring they can effectively manage their medication sensitivities without the need for in-person clinic visits.
Desensitization is a crucial procedure for those who need antibiotic allergy treatment despite their allergies. This process is part of the antibiotic allergy treatment, which entails gradually exposing the individual to the antibiotic under strict medical supervision, enabling them to develop tolerance over time. Recent studies indicate that desensitization protocols can be highly effective, with success rates reaching up to 98% in carefully monitored environments. A systematic review has shown that individuals undergoing desensitization experienced significantly improved outcomes, including a marked reduction in the occurrence of breakthrough reactions.
Current trends in desensitization underscore the importance of personalized care plans, often involving multidisciplinary teams to enhance safety and efficacy. Recent research suggests that non-allergist healthcare providers can successfully implement desensitization protocols, thereby expanding access to this essential care option. As resistance to medications continues to rise, the ability to safely desensitize individuals with sensitivities is becoming increasingly critical in clinical practice, ensuring that effective first-line treatments remain available. Additionally, the financial implications of managing drug sensitivities are substantial, with documented annual hospital medication savings ranging from $12,400 to $26,000. This factor is particularly relevant for HR Managers focused on cost-effective healthcare solutions. AllergenIQ's comprehensive strategy for thorough sensitivity management ensures that individuals receive the necessary support to manage their conditions effectively.
Implement Preventive Strategies for Managing Antibiotic Allergies
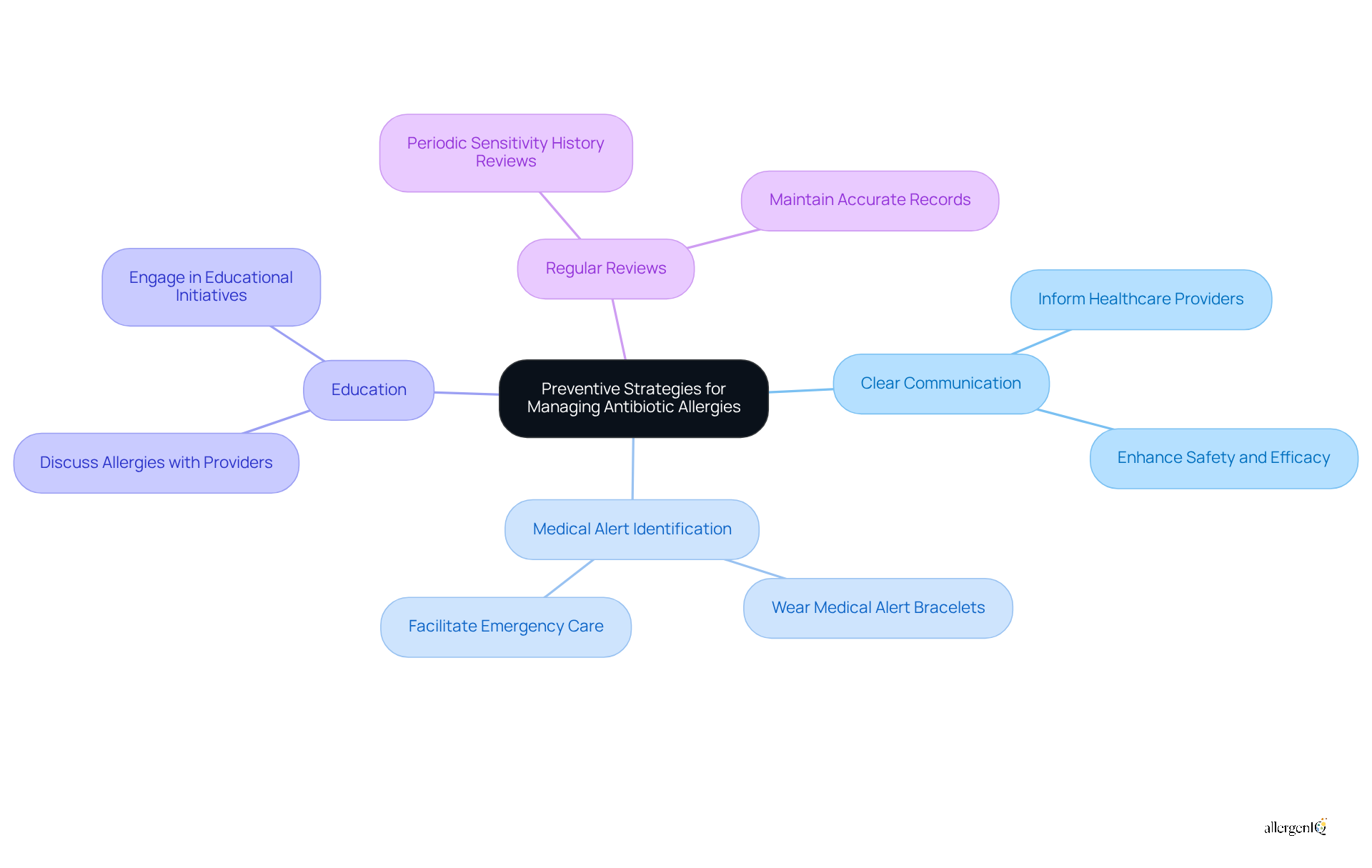
Establishing efficient preventive measures for managing drug sensitivities, such as antibiotic allergy treatment, is essential for ensuring safety and improving health outcomes. The following key strategies are recommended:
-
Clear Communication: Informing all healthcare providers about antibiotic allergies is vital. This practice ensures that everyone involved in a patient's care is aware of potential risks, thereby reducing the likelihood of adverse reactions. Healthcare professionals emphasize that effective communication can significantly enhance the safety and efficacy of antibiotic allergy treatment.
-
Medical Alert Identification: Wearing a medical alert bracelet that indicates drug sensitivities can be life-saving. This straightforward tool provides immediate information to healthcare providers in emergency situations, facilitating prompt and appropriate care.
Education about antibiotic allergy treatment is crucial for staying informed about potential allergens in medications. Engaging in discussions with healthcare providers about antibiotic allergy treatment can help avoid unnecessary exposure to allergens. Educational initiatives have shown that patients who are well-informed about their sensitivities are more likely to engage in proactive management.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically reviewing sensitivity history with healthcare providers is essential for maintaining accurate records and ensuring that treatment plans remain appropriate. Research indicates that consistent updates can lead to improved management of sensitivities and reduce the likelihood of mislabeling, a common issue in healthcare settings.
By adopting these strategies, patients can actively participate in their antibiotic allergy treatment and allergy management, enhancing communication with healthcare providers and improving overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
Antibiotic allergies pose a significant challenge in healthcare, impacting both patient safety and treatment efficacy. Mislabeling and misunderstanding of these allergies can lead to the unnecessary avoidance of effective medications, which in turn results in increased healthcare costs and prolonged illnesses. Therefore, understanding the nuances of antibiotic allergy management is crucial for improving patient outcomes and ensuring individuals receive the most effective treatment options available.
Key insights emphasize the importance of accurate diagnosis and treatment strategies. Early recognition of symptoms, the use of comprehensive diagnostic methods, and the implementation of tailored treatment plans - including desensitization protocols - can significantly enhance the management of antibiotic allergies. Additionally, preventive strategies such as clear communication, medical alert identification, and regular reviews of sensitivity history are essential for reducing the risk of adverse reactions and ensuring that patients are well-informed about their conditions.
Ultimately, addressing antibiotic allergies transcends individual care; it enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the healthcare system. By embracing current trends and guidelines in antibiotic allergy treatment, healthcare providers can ensure that patients receive appropriate care while minimizing the financial implications of mismanagement. Engaging in proactive management and education surrounding antibiotic allergies empowers both patients and healthcare professionals, leading to safer and more effective treatment outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are antibiotic allergies and their impact on healthcare?
Antibiotic allergies are negative immune responses to medications, with symptoms ranging from mild skin reactions to severe anaphylaxis. These sensitivities can lead to the unnecessary avoidance of effective medications, increasing medical costs and prolonging illness.
How prevalent are mislabeling and inaccuracies in antibiotic allergy classifications?
Approximately 10% to 20% of hospitalized patients are labeled allergic to beta-lactam medications, with over 90% of these classifications being inaccurate. This mislabeling can affect between 4,500 and 9,000 patients annually at institutions like Michigan Medicine.
What are the financial implications of being labeled with an antibiotic allergy?
Patients with a penicillin sensitivity incur higher medication costs, averaging $10.05 compared to $13.00 for those without such labels. Avoiding beta-lactam medications can lead to the use of less effective alternatives, increasing the risk of complications.
Why is it important to identify antibiotic sensitivities?
Identifying antibiotic sensitivities is crucial for effective treatment and improving patient outcomes. A systematic approach to evaluating and correcting incorrect sensitivity labels can enhance infection management and reduce healthcare expenses.
What percentage of patients experience adverse reactions during drug challenges for beta-lactam sensitivities?
Research indicates that 98% of patients who underwent drug challenges for beta-lactam sensitivities did so without adverse reactions, highlighting the potential for safe de-labeling.
Can you provide an example of a successful medication sensitivity management strategy?
The Beta-Lactam Allergy Evaluation Service has effectively identified true sensitivities and removed labels from individuals who are not sensitive, improving treatment options for thousands and enhancing medication management.
What are the common symptoms of antibiotic allergies?
Common symptoms include skin reactions (hives, rashes, itching), respiratory issues (wheezing, difficulty breathing), gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), and anaphylaxis (swelling, rapid heartbeat, loss of consciousness).
How quickly can anaphylaxis occur after contact with an allergen?
Anaphylaxis can occur within minutes to hours after contact with the allergen, making quick recognition and intervention essential.
What is the significance of early identification of antibiotic allergy symptoms?
Early identification leads to faster care, as 42% of people seek medical attention within 15 minutes of symptom onset, emphasizing the importance of awareness in managing medication sensitivities.




