Introduction
Food color allergies, often overlooked, can provoke severe immune reactions in susceptible individuals, particularly children. Artificial dyes such as Red 40 and Yellow 5 are prevalent in many popular products, making it essential for affected individuals to understand the symptoms and management strategies.
How can individuals navigate the complexities of food color allergies while ensuring safety and enjoyment of their favorite foods? This article explores the nuances of food color allergies, providing insights into recognition, management, and personalized testing strategies designed to empower those at risk.
Define Food Color Allergy: Understanding the Basics
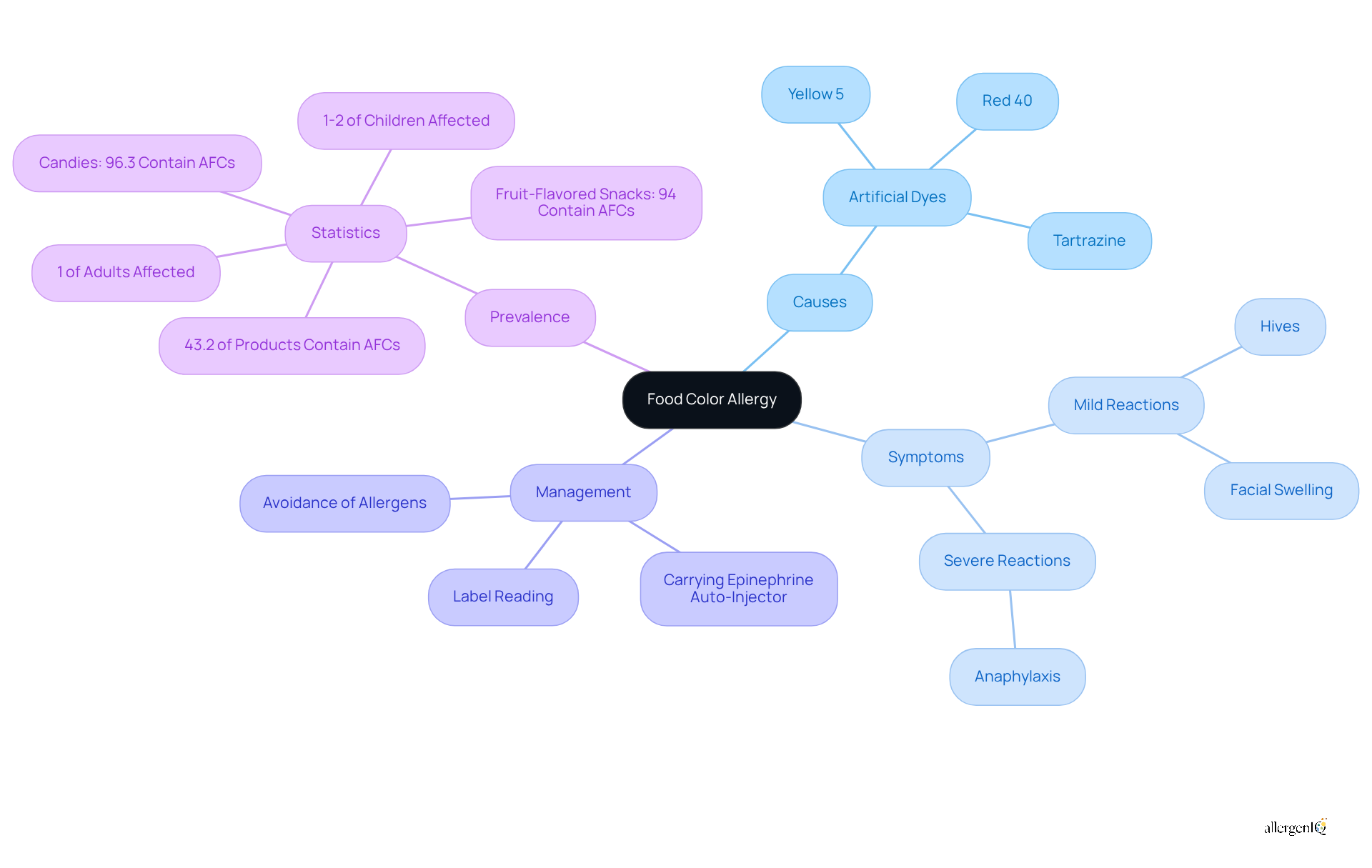
An adverse immune reaction can be triggered by certain artificial dye additives in various products and beverages, especially for those with a food color allergy. Red 40, Yellow 5, and Tartrazine are common offenders associated with food color allergy. Unlike dietary intolerances, which may cause discomfort without an immune response, reactions to these additives can provoke severe consequences, including anaphylaxis. Approximately 1-2% of children and about 1% of adults in the U.S. are affected by food color allergy, which underscores the importance of awareness and effective management strategies.
The immune reaction to dietary additives occurs when the body mistakenly identifies these substances as harmful, leading to the release of histamines and other chemicals that trigger allergic symptoms. These symptoms can range from mild reactions, such as hives and facial swelling, to severe anaphylactic incidents that require immediate medical attention.
Effective management of food color allergy, particularly in children, necessitates strict avoidance of known allergens and meticulous reading of product labels. Parents and caregivers are advised to consult with allergists to develop tailored management plans. Specialists emphasize that vigilance in monitoring consumption levels and ingredient lists is crucial for preventing allergy occurrences. Furthermore, individuals with a history of severe reactions are recommended to carry an epinephrine auto-injector.
Recent studies indicate that synthetic dyes, which are linked to food color allergy, are prevalent in many products targeted at children, with candies and fruit-flavored treats exhibiting particularly high levels of these additives. This situation highlights the need for collaboration among clinicians, parents, and food manufacturers to minimize exposure to artificial food colors, thereby promoting healthier dietary options for children.
Identify Symptoms: Recognizing Food Color Allergy Reactions
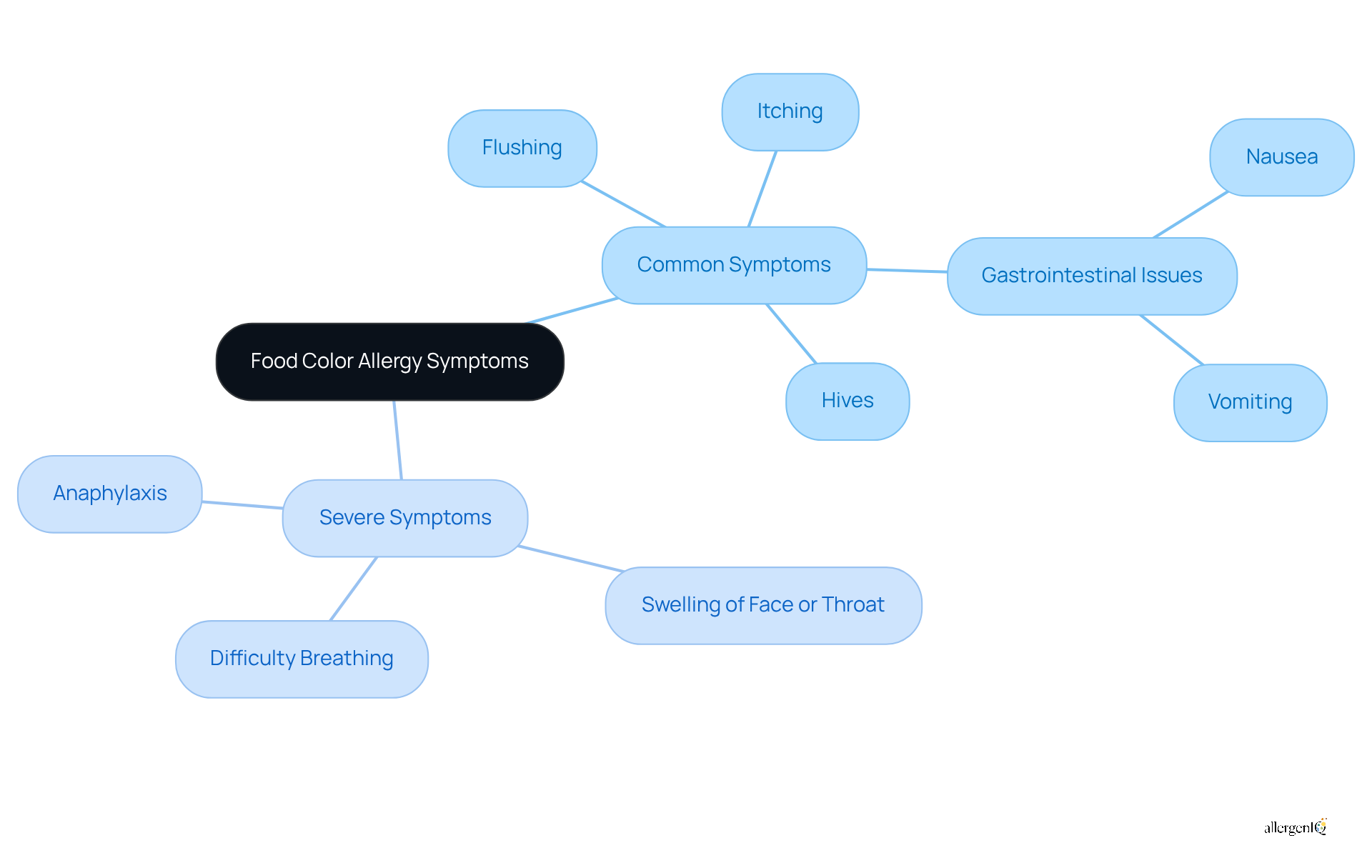
Food color allergy can provoke a range of responses, from mild to life-threatening. Common symptoms include:
- Hives
- Flushing
- Itching
- Gastrointestinal issues such as nausea or vomiting
In severe cases, individuals may experience:
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the face or throat
- Anaphylaxis, which necessitates immediate medical intervention
Awareness of these symptoms is essential, as severe allergic responses can escalate quickly.
For instance, some individuals have reported a rapid onset of symptoms after consuming products containing dye additives, underscoring the need for caution. Maintaining a dietary diary can assist in monitoring reactions and recognizing potential allergens. Healthcare experts emphasize the importance of identifying these signs promptly to ensure timely care, particularly in situations where contact with additive substances is suspected. As awareness increases, it becomes increasingly vital for individuals to educate themselves about the potential risks associated with color additives and food color allergy, and to seek medical counsel when necessary.
Manage Food Color Allergies: Effective Strategies and Solutions
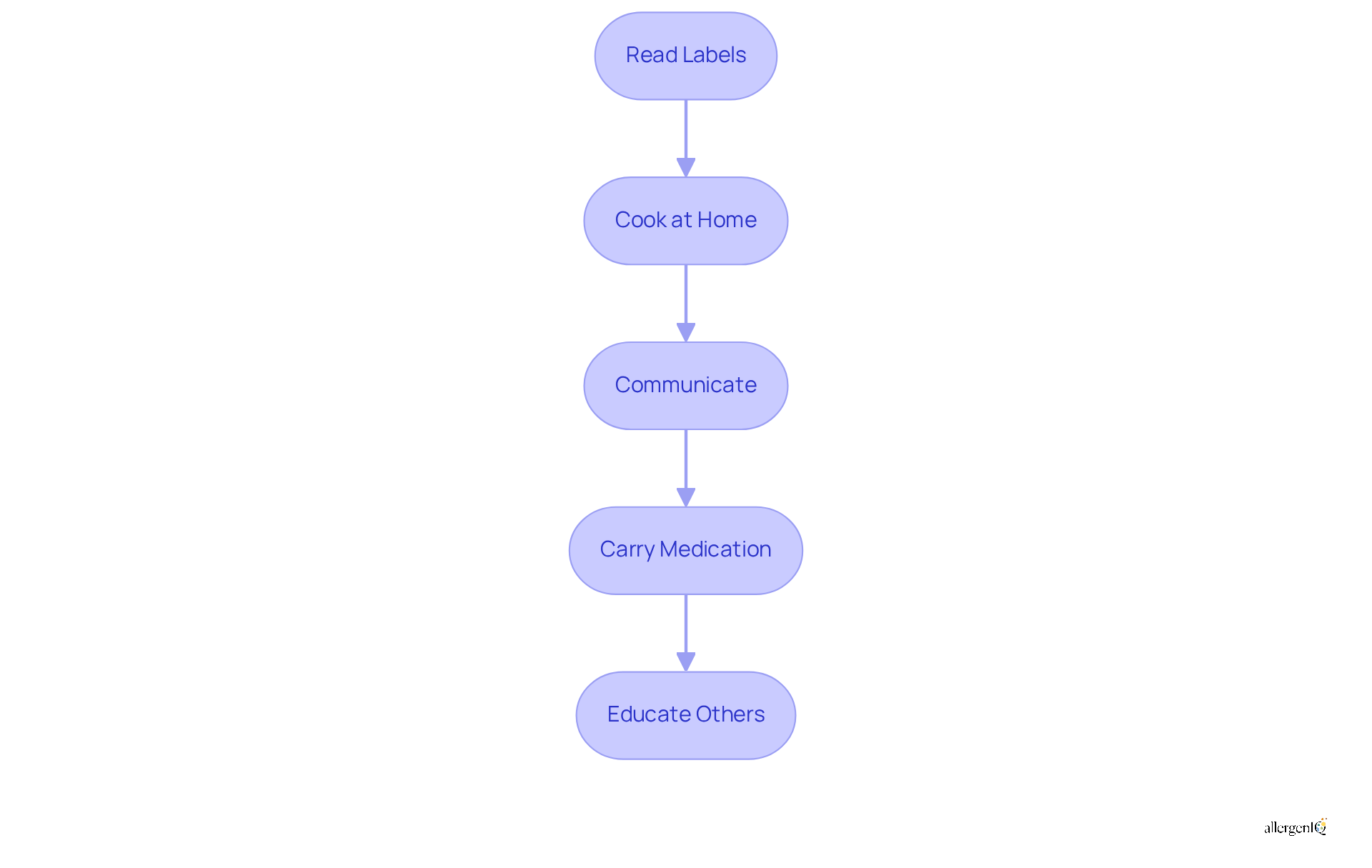
To effectively manage food color allergies, individuals should implement the following strategies:
-
Read Labels: Always scrutinize ingredient lists for artificial color additives before consuming any packaged items. This practice is crucial, as even trace amounts of allergens related to food color allergy can trigger severe reactions.
-
Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home provides greater control over ingredients, significantly reducing the risk of accidental exposure to allergens. Home cooking not only allows for safer meal preparation but also encourages healthier eating habits.
-
Communicate: Clearly inform restaurants and food providers about your sensitivity to ensure safe meal preparation. Effective communication can prevent misunderstandings and help ensure that your dietary needs, particularly in relation to a food color allergy, are met.
-
Carry Medication: Always have antihistamines or an epinephrine auto-injector readily available in case of accidental exposure. Being prepared can be life-saving in emergency situations.
-
Educate Others: Inform family, friends, and caregivers about your sensitivity and its potential severity. Educating your support network fosters a safer environment and encourages vigilance in avoiding food color allergy.
By adopting these strategies, individuals can significantly improve their sensitivity management and reduce the risk of negative responses.
Utilize Personalized Testing: Tailoring Allergy Management Plans
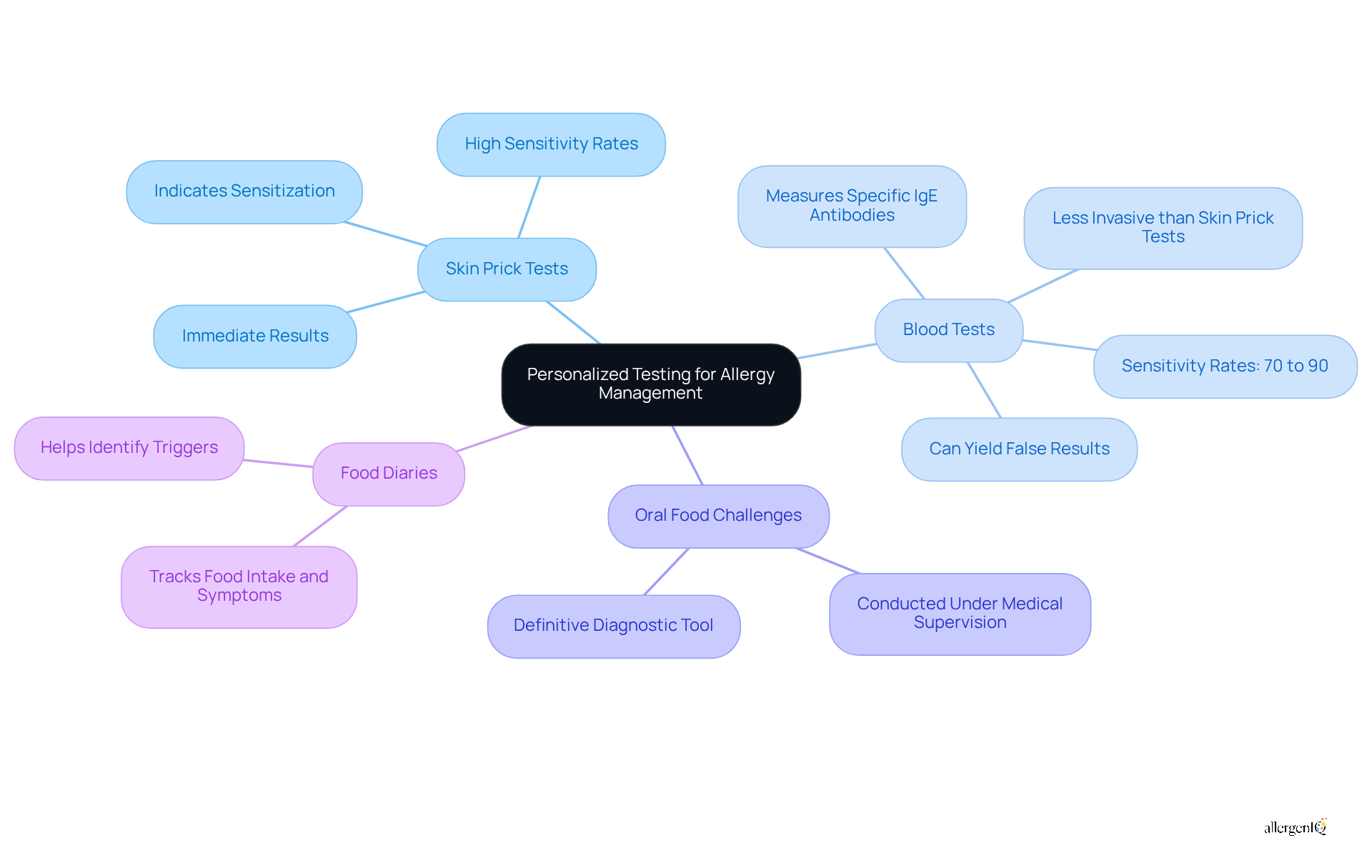
Customized testing is crucial for accurately identifying sensitivities related to food color allergy. The primary methods include:
- Skin Prick Tests: This method entails applying small amounts of allergens to the skin and observing for reactions, yielding immediate results that indicate sensitization. Skin prick tests have shown high sensitivity rates, establishing them as a reliable option for diagnosing dietary sensitivities.
- Blood Tests: These tests assess specific IgE antibodies in response to allergens, providing insights into the severity of the allergy. Blood tests are generally considered precise, with sensitivity rates ranging from 70% to 90%. They can detect a wide array of allergens, including those related to food color allergy.
- Oral Food Challenges: Conducted under medical supervision, this method involves consuming small amounts of the suspected allergen to monitor for reactions, serving as a definitive diagnostic tool.
- Food Diaries: Maintaining a detailed record of food intake and symptoms can assist in identifying triggers and informing management strategies.
By employing these testing methods, individuals can formulate tailored management plans that effectively address their specific allergies, ultimately enhancing their quality of life.
Conclusion
Food color allergy poses a significant health concern, particularly for individuals who experience adverse reactions to artificial dye additives. Understanding this allergy's nature, including its symptoms and management strategies, is essential for affected individuals and families. The importance of awareness and proactive measures cannot be overstated, especially considering the prevalence of these additives in many everyday products.
Key points include the range of symptoms associated with food color allergies, which can vary from mild irritations to severe anaphylactic reactions. Effective management strategies such as reading labels, cooking at home, and maintaining open communication with food providers empower individuals to navigate their dietary restrictions safely. Additionally, personalized testing methods play a crucial role in accurately identifying sensitivities and tailoring management plans that enhance quality of life.
Ultimately, managing food color allergies requires a collaborative effort among individuals, healthcare providers, and food manufacturers. By prioritizing education and vigilance, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of exposure to harmful additives. Embracing these strategies not only fosters a safer environment but also promotes healthier choices, ensuring that those affected can lead fulfilling lives without the fear of allergic reactions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a food color allergy?
A food color allergy is an adverse immune reaction triggered by certain artificial dye additives found in various products and beverages, leading to symptoms that can range from mild to severe.
What are common artificial dyes associated with food color allergies?
Common offenders associated with food color allergies include Red 40, Yellow 5, and Tartrazine.
How does a food color allergy differ from dietary intolerances?
Unlike dietary intolerances, which may cause discomfort without an immune response, food color allergies provoke an immune reaction that can lead to severe consequences, including anaphylaxis.
How prevalent is food color allergy in the U.S.?
Approximately 1-2% of children and about 1% of adults in the U.S. are affected by food color allergies.
What symptoms can occur due to a food color allergy?
Symptoms can range from mild reactions, such as hives and facial swelling, to severe incidents like anaphylaxis that require immediate medical attention.
How can food color allergies be managed effectively?
Effective management requires strict avoidance of known allergens, meticulous reading of product labels, and consultation with allergists to develop tailored management plans.
What precautions should individuals with a food color allergy take?
Individuals with a history of severe reactions are recommended to carry an epinephrine auto-injector for emergency situations.
Why are synthetic dyes a concern, particularly for children?
Synthetic dyes linked to food color allergies are prevalent in many products targeted at children, such as candies and fruit-flavored treats, highlighting the need for careful monitoring of these additives.
What is the role of collaboration in managing food color allergies?
Collaboration among clinicians, parents, and food manufacturers is essential to minimize exposure to artificial food colors and promote healthier dietary options for children.




