Introduction
Understanding the nuances of milk allergies is essential, particularly given the prevalence of dairy products in our diets. For many individuals, consuming milk can lead to a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild hives to severe anaphylaxis. Therefore, it is critical to recognize and effectively manage these reactions. This article explores the symptoms associated with milk allergies. It outlines management strategies, and discusses preventive measures. It raises an important question: how can individuals and families navigate the complexities of milk allergies and milk intolerances to ensure their safety and well-being?
Define Milk Allergy: Understanding the Basics
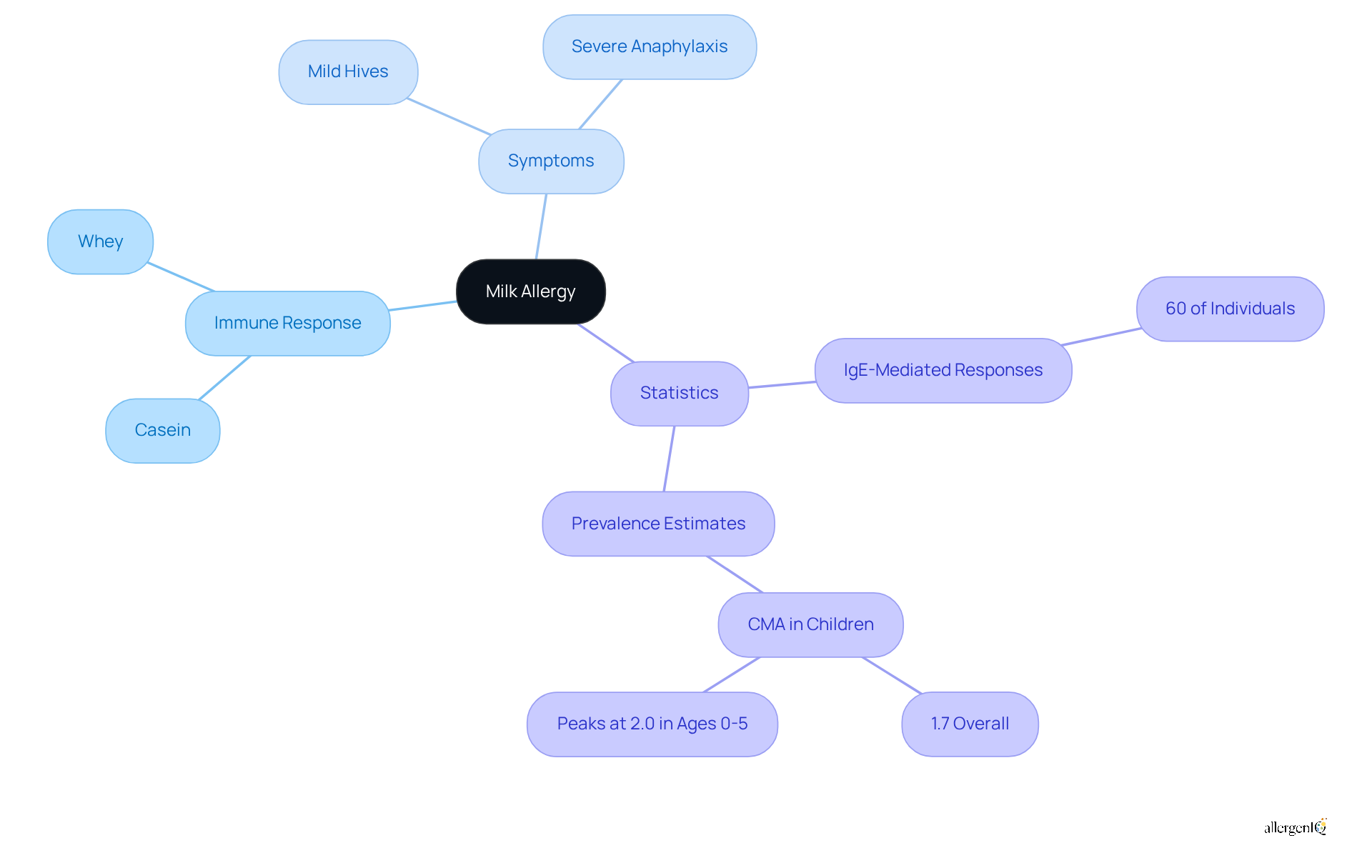
Milk allergy represents an atypical immune response to proteins found in cow's dairy, primarily casein and whey. For individuals with this allergy the immune system mistakenly identifies these proteins as harmful invaders, leading to an allergic reaction upon milk protein consumption. Symptoms of milk allergy can vary significantly, from mild hives to severe anaphylaxis, highlighting the importance of effective recognition and management of the condition by those affected.
Recent studies indicate that around 60% of individuals with reactions to cow's milk exhibit IgE-mediated responses, which may manifest within minutes to hours following dairy intake. Understanding these fundamental aspects is essential for implementing avoidance strategies and ensuring proper management of milk allergy.
Identify Symptoms: Recognizing Milk Allergic Reaction:
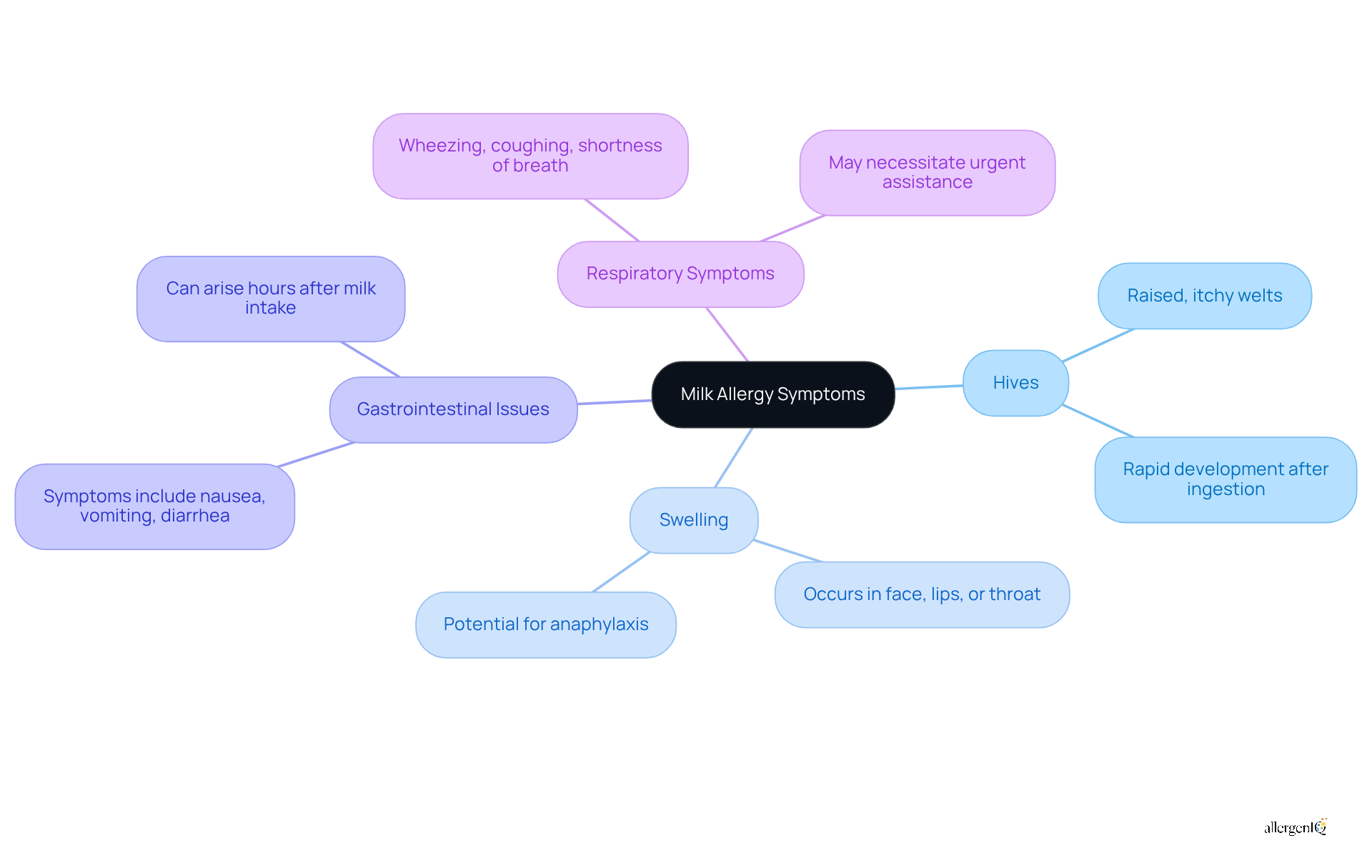
Common signs of milk allergy symptoms include:
- Hives: Raised, itchy welts on the skin that can appear suddenly, often as a reaction to milk proteins. In children, these can be particularly alarming, as they may develop rapidly after ingestion.
- Swelling: This may occur in areas such as the face, lips, or throat, potentially leading to difficulty breathing. Such swelling is a critical indicator of anaphylaxis, which requires immediate medical attention.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea may accompany skin responses, indicating a systemic reaction to the allergen. In certain instances, these signs can arise hours after milk intake, complicating diagnosis.
- Respiratory Symptoms: Wheezing, coughing, or shortness of breath can signal a more severe allergic reaction. These signs are especially concerning, as they may intensify rapidly and necessitate urgent assistance, such as anaphylaxis management.
Identifying these signs early are essential for effective management and treatment. Recent studies indicate that milk allergy hives are a common symptoms experienced by both children and adults with milk allergies. Research shows that approximately 60% of individuals with cow's dairy intolerance experience IgE-mediated responses, frequently involving skin manifestations. Understanding these signs empowers families to act swiftly, ensuring safety and reducing the risk of severe allergic reactions.
For those concerned about milk allergies, AllergenIQ offers specialized food allergy testing to identify specific triggers. By completing a detailed online survey and scheduling a virtual consultation with a specialist, families can obtain a customized treatment plan tailored to their needs. This proactive approach not only addresses issues but also provides ongoing support, enabling families to adjust their plans as necessary and effectively manage their food allergies.
Manage Symptoms: Effective Strategies for Milk Allergy Hives
To effectively manage symptoms of milk allergies, consider the following strategies:
-
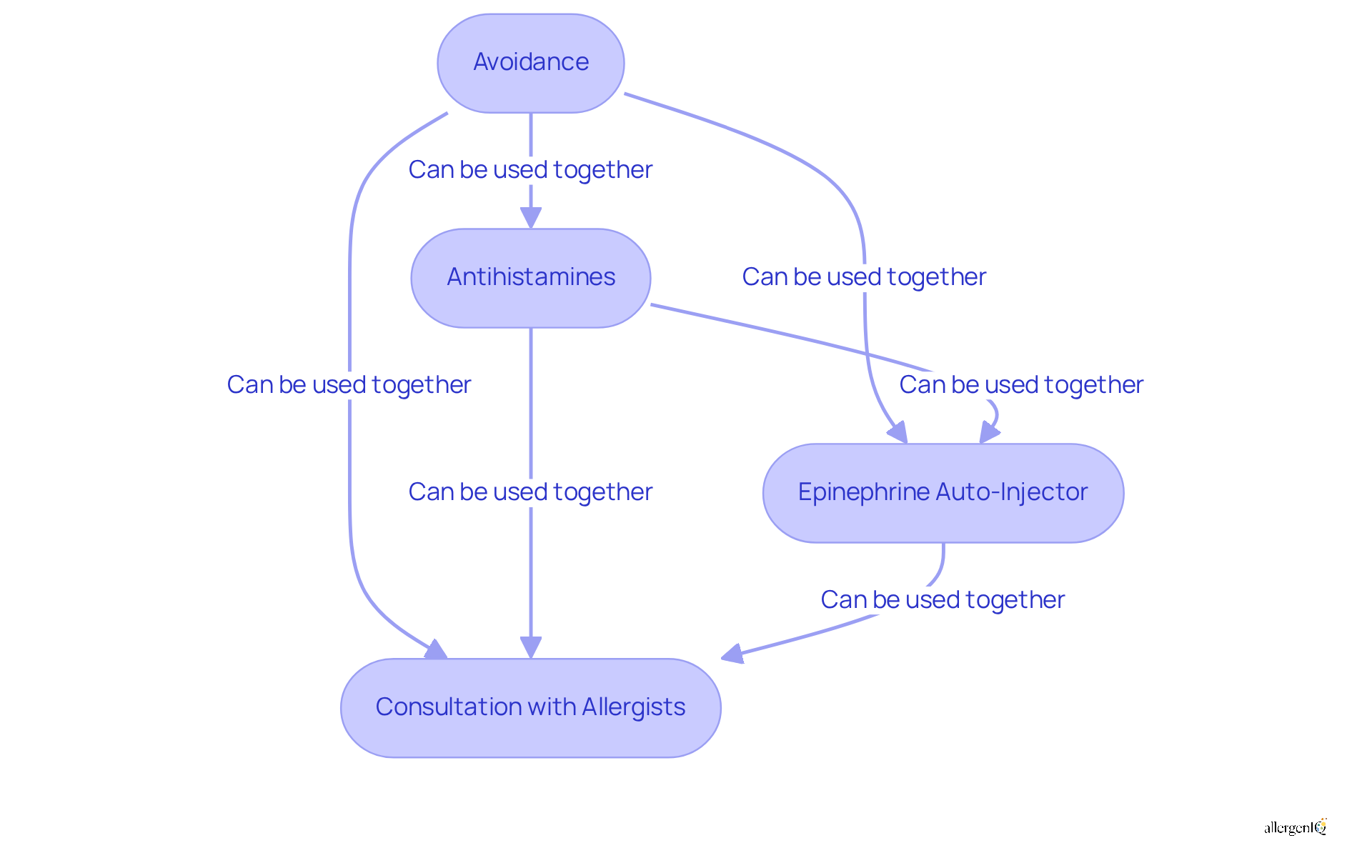
Avoidance: The most effective way to prevent allergic reactions is to avoid all foods that contain milk protein It is crucial to read labels carefully to identify hidden sources of milk, as it can be present in unexpected foods.
-
Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines can alleviate mild issues such as hives and itching caused by a milk allergy. These medications function by blocking histamine, a substance in the body that triggers allergic symptoms. Consulting with a healthcare provider for specific recommendations tailored to individual needs is advisable. Allergists emphasize that while antihistamines can be beneficial for managing mild responses, they should not replace emergency care for severe food allergy.
-
Epinephrine Auto-Injector: For individuals at risk of severe reactions, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector is essential. This device can quickly treat symptoms of anaphylaxis, which may develop within minutes of exposure to milk proteins. Current guidelines recommend that individuals diagnosed with milk allergies must always carry an auto-injector set and be trained in its use.
-
Consultation with Allergists: Regular consultations with an allergist can help develop a management plan tailored to individual needs. This may involve discussions about potential desensitization therapies, which aim to increase tolerance to milk proteins over time. Staying informed about the latest guidelines for dairy intolerance avoidance and management is vital for maintaining health and wellness.
Prevent Hives: Long-Term Management of Milk Allergies
Effective long-term management of milk allergies necessitates a multifaceted approach that encompasses several key strategies:
-
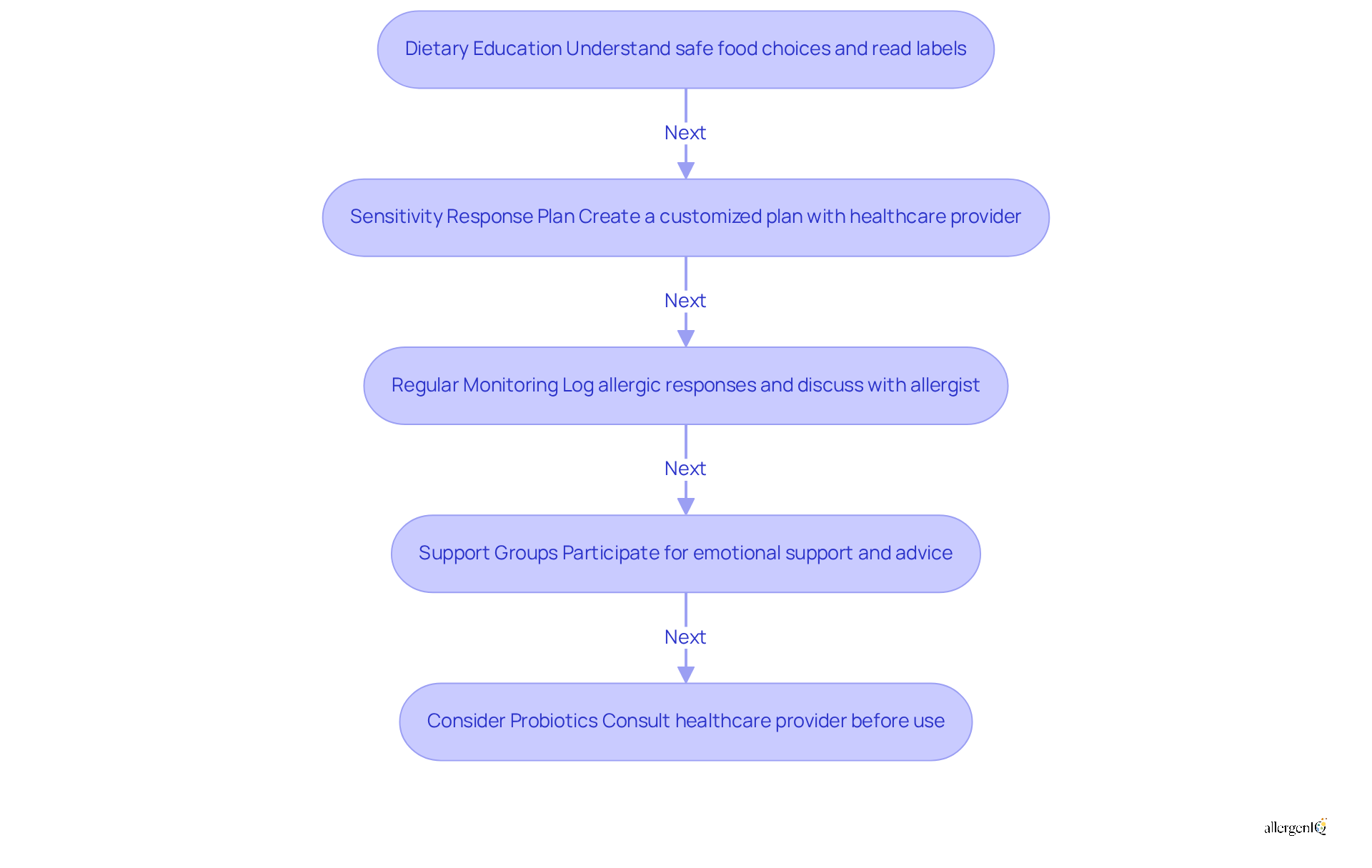
Dietary Education: Families must comprehend safe food choices and learn to accurately read food labels to avoid milk proteins. Dietitians highlight that thorough dietary education empowers families to make informed decisions, thereby reducing the risk of accidental exposure.
-
Food Allergy Anaphylaxis Response Plan: Collaborate with your healthcare provider to create a customized food allergy anaphylaxis plan. This plan should delineate specific steps to take in the event of exposure, ensuring that all individuals involved in the patient's care are prepared to respond appropriately. At AllergenIQ, we stress the importance of developing a tailored plan that reflects your unique triggers and needs.
-
Regular Monitoring: Keep a detailed log of any allergic responses and discuss these with your allergist. This ongoing dialogue facilitates adjustments to your management plan, ensuring its effectiveness as circumstances evolve. Our virtual consultations simplify the process of staying connected and updating your plan based on your experiences.
-
Support Groups: Participation in support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from others with similar experiences. These communities are invaluable for exchanging strategies and coping mechanisms. AllergenIQ also offers resources to help you connect with community support.
-
By implementing these strategies, individuals and families can more effectively navigate the complexities of milk allergy hives, enhancing their quality of life and minimizing the risk of severe allergic reactions.
Conclusion
This article has examined the fundamentals of milk allergy, including its definition, symptoms, and effective management strategies. By recognizing the immune response to dairy proteins and the potential severity of reactions, individuals can take informed steps to protect their health.
Key insights discussed include the importance of identifying symptoms such as:
- hives
- swelling
- gastrointestinal issues
- respiratory problems
The article emphasizes the necessity of:
- avoidance strategies
- the use of antihistamines
- the critical role of epinephrine auto-injectors for severe reactions
Regular consultations with allergists and the development of tailored management plans can significantly enhance the quality of life for those living with milk allergies.
Ultimately, effective long-term management of milk allergies requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
- dietary education
- regular monitoring
- community support
By implementing these strategies, individuals and families can navigate the challenges posed by milk allergy hives more effectively, ensuring a safer and healthier lifestyle. These steps not only reduce the risk of severe allergic reactions but also empower those affected to live more fully and confidently.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a milk allergy?
A milk allergy is an atypical immune response to proteins found in cow's dairy, primarily casein and whey, where the immune system mistakenly identifies these proteins as harmful, leading to allergic reactions upon dairy consumption.
What are the symptoms of milk allergy?
Symptoms of milk allergy can vary significantly, ranging from mild hives to severe anaphylaxis.
How common are IgE-mediated responses in individuals with cow's dairy intolerance?
Recent studies indicate that around 60% of individuals with cow's dairy intolerance exhibit IgE-mediated responses.
How quickly can symptoms appear after consuming dairy for those with a milk allergy?
Symptoms may manifest within minutes to hours following dairy intake.
Why is it important to understand milk allergy?
Understanding milk allergy is essential for implementing avoidance strategies and ensuring proper management of dairy sensitivities.




