Introduction
An increasing number of individuals are recognizing sensitivities to walnuts, a type of tree nut that can provoke a range of allergic reactions. It is essential for those affected to understand the symptoms and management strategies associated with walnut allergy, as these reactions can vary from mild discomfort to severe, life-threatening anaphylaxis.
How can one effectively navigate the complexities of this allergy, particularly given the significant risks involved? This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of walnut allergies, providing readers with vital information to:
- Identify symptoms
- Pursue accurate diagnosis
- Adopt effective management strategies
Define Walnut Allergy: Key Concepts and Overview
A sensitivity to walnuts is classified as a type of tree nut sensitivity, wherein the immune system erroneously identifies proteins in these nuts as harmful agents. This immune response is primarily mediated by Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies, which trigger a range of symptoms of walnut allergy when exposed to nuts. Reactions can differ significantly, ranging from mild symptoms of walnut allergy like itching and hives to severe, life-threatening conditions such as anaphylaxis. Notably, tree nuts, including walnuts, account for 18-40% of food-related fatalities due to anaphylaxis, underscoring the critical need for awareness and education regarding these sensitivities.
Recent research indicates an increasing prevalence of sensitivities to walnuts, with estimates suggesting that approximately 1.1% of children in the U.S. are affected. This upward trend emphasizes the necessity for early diagnosis and intervention. Effective management strategies involve:
- Avoiding these nuts and products containing them
- Educating patients and caregivers on recognizing the symptoms of walnut allergy
- Using epinephrine auto-injectors in emergencies
Experts assert that understanding the immune response associated with nut sensitivities is vital for developing effective treatment strategies. For instance, allergists note that the severity of allergic reactions correlates closely with specific allergenic components found in nuts. Successful diagnosis and treatment in real-world scenarios often involve a combination of:
- Skin prick tests
- Oral food challenges
These methods aid in confirming the condition and informing dietary restrictions. By fostering a deeper understanding of nut sensitivities, individuals can more adeptly navigate their dietary choices and manage their health.
Identify Symptoms of Walnut Allergy: Common Reactions and Signs
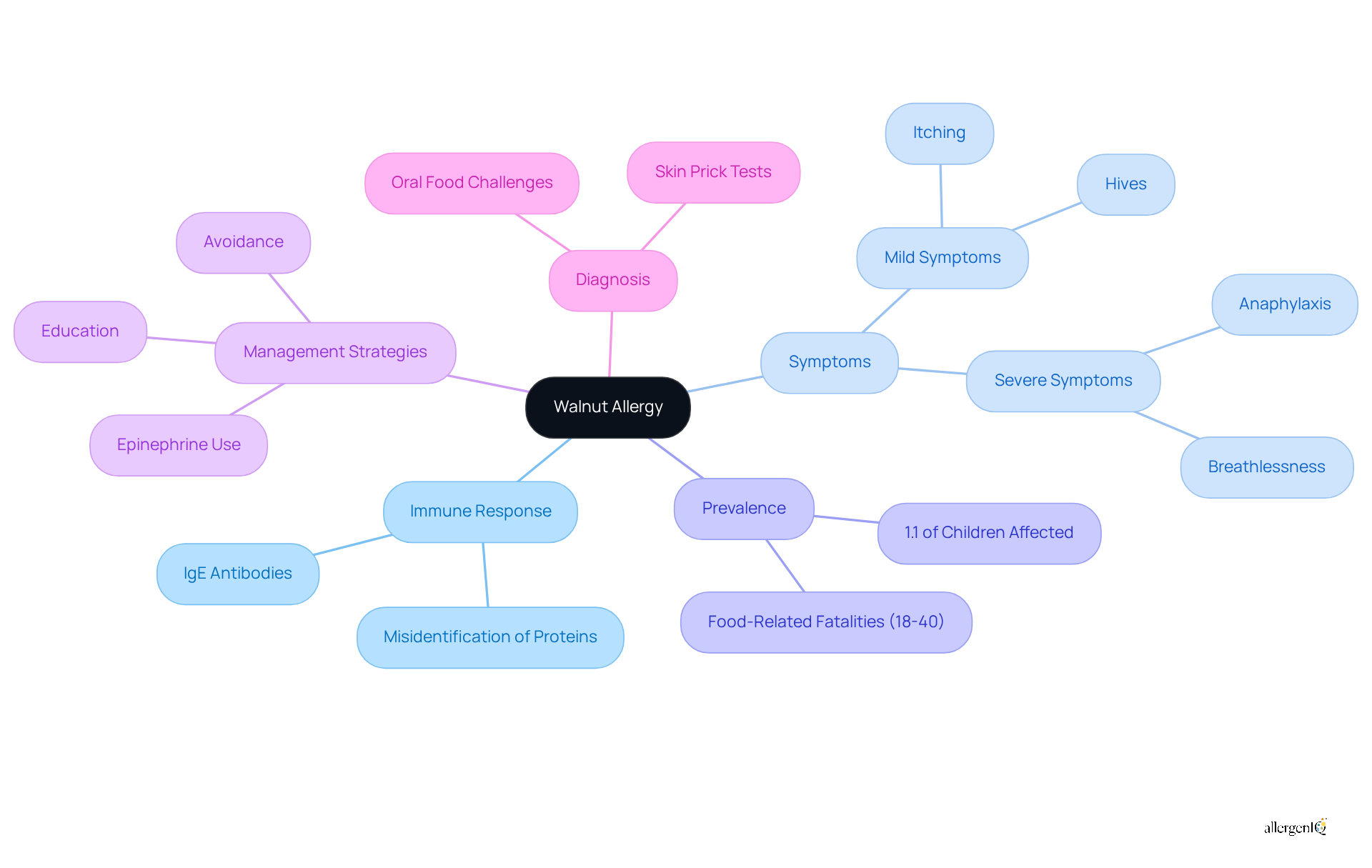
Symptoms of walnut allergy can manifest in various ways, making recognition crucial for effective management. Common symptoms include:
- Oral Symptoms: Individuals may experience itching or tingling sensations in the mouth, throat, or ears shortly after exposure to walnuts.
- Skin Reactions: Hives, redness, or swelling (angioedema) can occur, indicating an allergic response.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms of walnut allergy, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or diarrhea, may arise, reflecting the body's response to walnut proteins.
- Respiratory Symptoms: Allergic responses can lead to coughing, wheezing, nasal congestion, or difficulty breathing, which may escalate quickly.
- Anaphylaxis: This severe, life-threatening reaction can include difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, rapid pulse, and loss of consciousness. Anaphylaxis represents a significant concern, as it accounts for a considerable portion of nut sensitivity cases, necessitating prompt medical intervention.
Real-life examples underscore the importance of awareness and preparedness. For instance, individuals with nut sensitivities must scrutinize ingredient labels carefully, as these nuts can be hidden in various foods, including baked goods and sauces. Cross-contamination poses another risk, often occurring when non-walnut foods are prepared using the same utensils as walnut-containing products.
Recent insights from allergists emphasize that the risk of anaphylaxis varies by nut type and age, highlighting the need for careful observation, particularly in children with multiple nut sensitivities. Approximately 0.5 to 1 percent of the U.S. population is affected by nut sensitivities, exhibiting symptoms of walnut allergy that can range from mild to severe. Understanding these signs and their implications is essential for anyone managing nut sensitivities, ensuring timely action and safety.
Explore Diagnosis of Walnut Allergy: Testing and Evaluation Methods
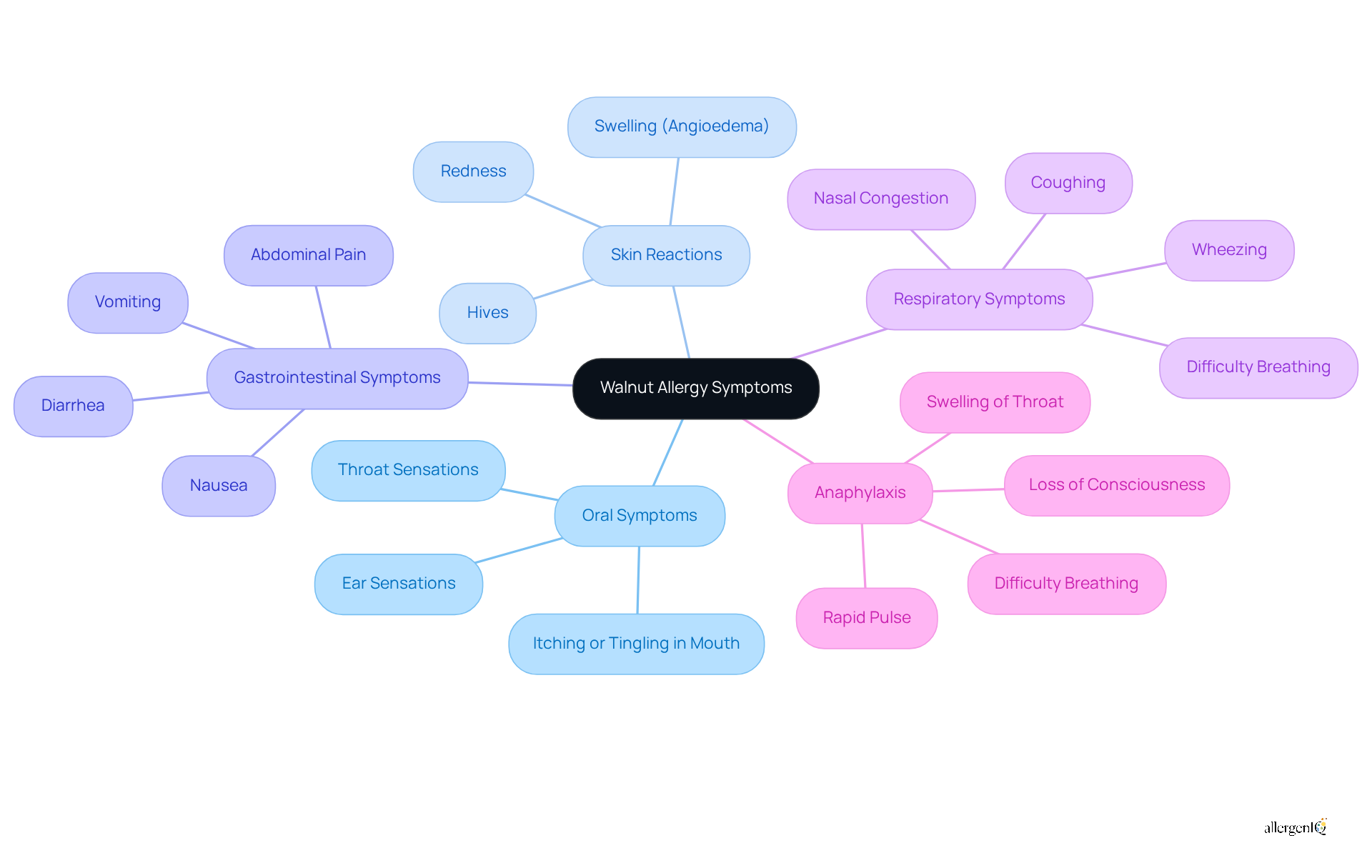
Diagnosing walnut allergy typically involves several methods that ensure accurate identification of the symptoms of walnut allergy and effective management of the condition.
-
Skin Prick Tests: This method entails applying small amounts of walnut extract to the skin and observing for allergic reactions. Recent studies indicate that skin prick tests exhibit diagnostic performance comparable to specific IgE tests, with slightly better results for the latter. Notably, the prick-by-prick (PbP) test has shown promise in diagnosing nut allergies, correlating well with outcomes from oral food challenges.
-
Blood Tests: These tests measure the presence of IgE antibodies specific to nut proteins. Elevated levels of specific IgE can suggest an increased risk of hypersensitivity responses. For instance, an IgE level exceeding 0.35 kUA/L to tree nut proteins indicates sensitivity, providing a reliable measure for diagnosis.
-
Oral Food Challenge (OFC): Conducted under medical supervision, this test involves the consumption of nuts to monitor for allergic reactions. While OFCs are regarded as the gold standard for verifying food sensitivities, they carry inherent risks, prompting a preference for alternative testing methods.
-
Component Testing: This advanced technique detects specific proteins in nuts that provoke allergic reactions, assisting in evaluating the intensity of the sensitivity. Understanding which proteins elicit reactions can provide insights into the symptoms of walnut allergy, thereby informing treatment decisions and dietary restrictions.
Precise identification is essential for the effective management and therapy of nut sensitivities. The NUT CRACKER study has validated a diagnostic algorithm that significantly reduces the need for oral food challenges, achieving an almost 80% reduction in required tests while maintaining high diagnostic accuracy with only 2.5% false positives. This innovative strategy underscores the importance of advancing testing techniques in managing sensitivities, ensuring patients receive timely and appropriate care.
Implement Management Strategies for Walnut Allergy: Treatment and Care Options
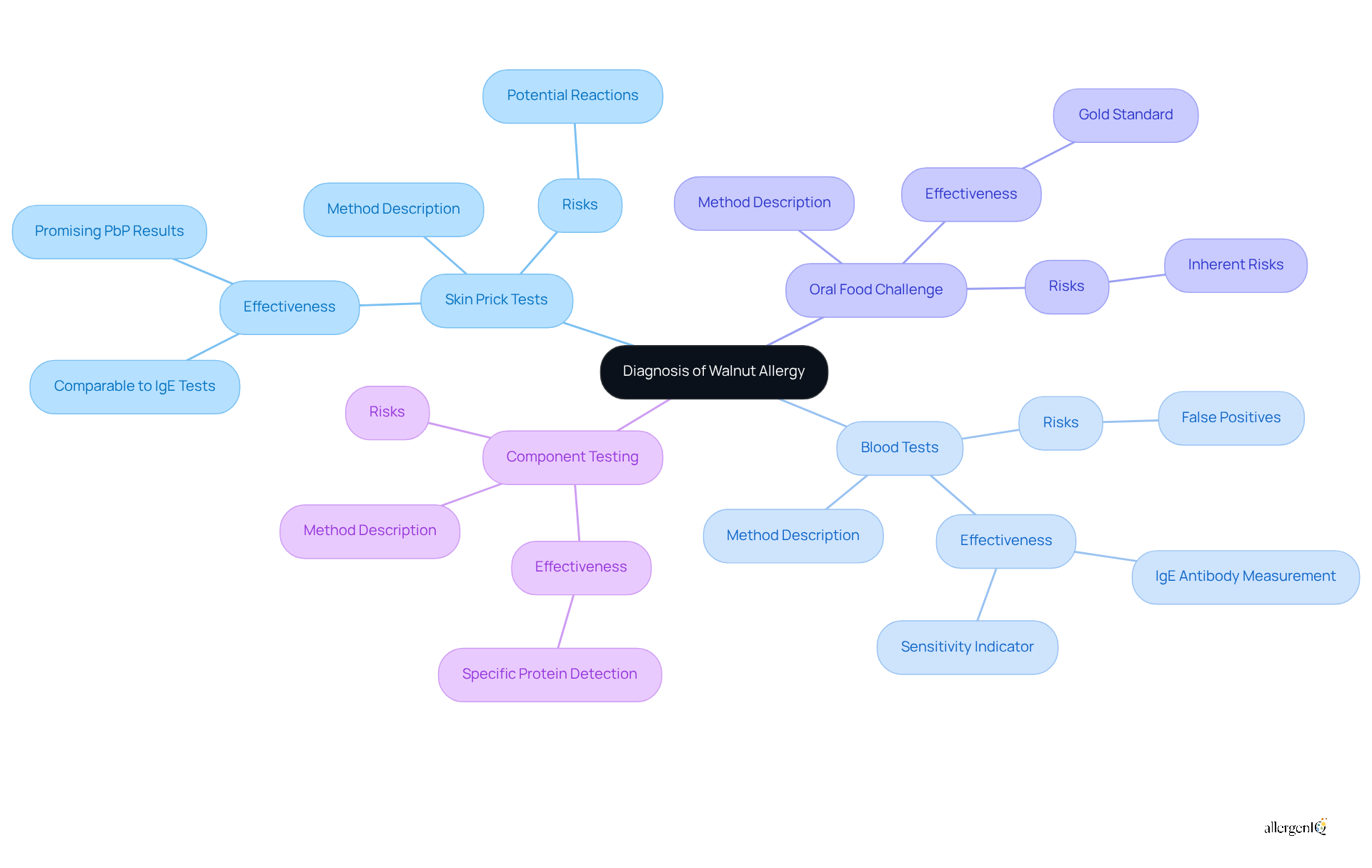
Managing walnut allergy effectively requires a multifaceted approach:
-
Avoidance: The cornerstone of prevention is strict avoidance of walnuts and walnut-containing products. It is crucial to scrutinize food labels to ensure safety.
-
Emergency Action Plan: Develop a comprehensive emergency action plan that includes carrying an epinephrine auto-injector, such as an EpiPen, to respond promptly to severe hypersensitivity. Research indicates that immediate use of epinephrine significantly reduces the risk of hospitalization and mortality associated with anaphylaxis.
-
Antihistamines: For mild allergic reactions, over-the-counter antihistamines can alleviate symptoms such as itching and hives.
-
Oral Immunotherapy: This innovative treatment involves the gradual introduction of small amounts of nuts under medical supervision, aiming to build tolerance over time. Recent studies have shown promising results, with 64% of children able to consume allergens freely after therapy.
-
Education: It is essential to inform family, friends, and caregivers about nut sensitivities and the appropriate responses in emergencies. A confirmed food sensitivity anaphylaxis action plan enables individuals to identify symptoms of walnut allergy and respond quickly, thereby decreasing unnecessary emergency room visits.
Understanding and implementing these management strategies are vital for individuals living with walnut allergies, ensuring their safety and enhancing their quality of life.
Conclusion
A walnut allergy poses a significant health concern that necessitates a comprehensive understanding and effective management. The immune system's erroneous identification of walnut proteins as threats can result in a range of reactions, from mild discomfort to severe anaphylaxis. Awareness of this allergy is particularly crucial, given its increasing prevalence among children and the potential for life-threatening consequences.
Key aspects of walnut allergy include its symptoms, diagnostic methods, and management strategies. Recognizing the various manifestations of this allergy - ranging from oral and skin reactions to gastrointestinal and respiratory symptoms - is essential for timely intervention. Diagnostic techniques such as skin prick tests, blood tests, and oral food challenges are vital in confirming sensitivities. Effective management strategies emphasize avoidance, emergency preparedness, and education.
Ultimately, understanding walnut allergy extends beyond merely identifying symptoms; it empowers individuals and families to navigate this challenge safely. By fostering awareness and implementing proactive management strategies, those affected can significantly enhance their quality of life and mitigate the risk of severe allergic reactions. Awareness and education are paramount - take action today to ensure a safer tomorrow for those living with walnut allergies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a walnut allergy?
A walnut allergy is a sensitivity to walnuts classified as a type of tree nut sensitivity, where the immune system mistakenly identifies proteins in walnuts as harmful, leading to an immune response mediated by Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies.
What are the symptoms of walnut allergy?
Symptoms of walnut allergy can vary widely and may include mild reactions such as itching and hives, as well as severe, life-threatening conditions like anaphylaxis.
How prevalent is walnut allergy among children in the U.S.?
Recent estimates suggest that approximately 1.1% of children in the U.S. are affected by walnut allergies, indicating an increasing prevalence.
What are effective management strategies for walnut allergy?
Effective management strategies include avoiding walnuts and products containing them, educating patients and caregivers about recognizing symptoms, and using epinephrine auto-injectors in emergencies.
How are walnut allergies diagnosed?
Diagnosis of walnut allergies often involves a combination of skin prick tests and oral food challenges to confirm the condition and inform dietary restrictions.
Why is understanding the immune response important for walnut allergy treatment?
Understanding the immune response associated with nut sensitivities is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies, as the severity of allergic reactions is closely linked to specific allergenic components found in nuts.




