Introduction
Wheat allergy, characterized by an immune response to cereal proteins, impacts a considerable number of adults and can result in a variety of distressing symptoms. It is essential to understand the distinctions between wheat allergy, gluten intolerance, and celiac disease for effective management and treatment. Individuals face the challenge of accurately identifying symptoms and differentiating among these conditions to prevent misdiagnosis.
To ensure proper diagnosis and management, what steps can be taken?
Furthermore, how can individuals empower themselves to live well with these sensitivities?
Define Wheat Allergy and Its Distinctions
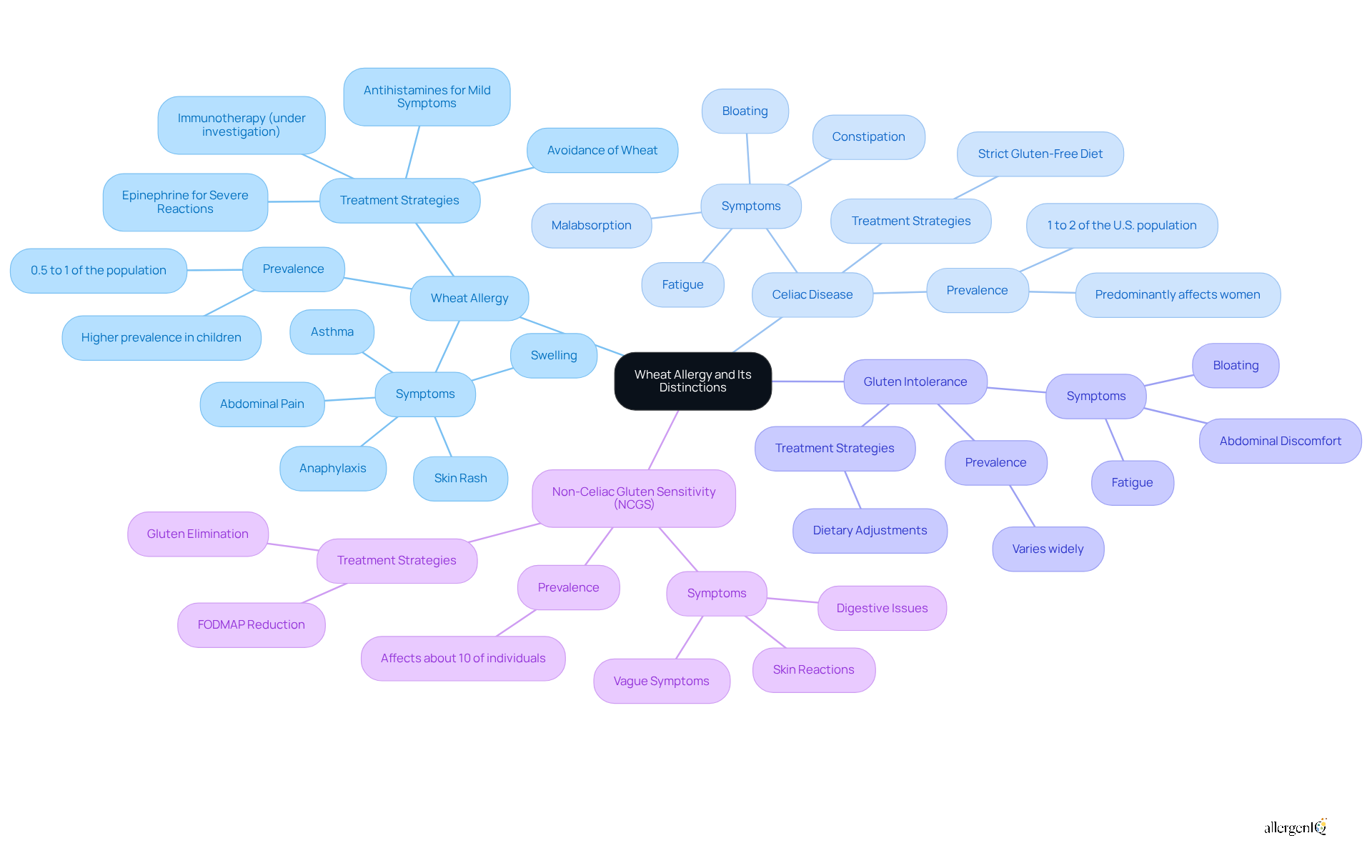
Wheat intolerance is an immune reaction triggered by the consumption of cereal proteins, leading to symptoms of wheat allergy in adults. This condition is characterized by an IgE-mediated response, which includes symptoms of wheat allergy in adults, wherein the immune system erroneously identifies grain proteins as harmful. In contrast, celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects approximately 1% to 2% of the U.S. population, predominantly impacting women. It arises when gluten consumption prompts the immune system to attack the small intestine's villi, resulting in malabsorption and a range of symptoms. This distinction is critical, as it influences treatment strategies, with the only effective management for celiac disease being a strict gluten-free diet.
Furthermore, gluten intolerance can manifest differently from non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), which does not involve an immune reaction but rather a sensitivity to gluten. NCGS affects about 10% of individuals without celiac disease or grain intolerance, with symptoms that may include bloating, abdominal discomfort, and fatigue. Diagnosing NCGS remains challenging due to its vague symptoms and the necessity to exclude other conditions.
Recent research underscores the importance of differentiating between these conditions. For instance, patients sensitive to grass pollen may be misdiagnosed as allergic to cereal grains due to significant cross-reactivity between cereal grain proteins and grass pollen proteins. This overlap can result in the over-diagnosis of wheat sensitivities, complicating effective management strategies. Understanding these distinctions is essential for developing customized treatment plans that address the specific needs of individuals affected by symptoms of wheat allergy in adults.
At AllergenIQ, we emphasize the importance of precise sensitivity testing and tailored treatment plans. Our at-home testing kits empower individuals to identify their specific allergens, while our online consultations provide the same quality of care as in-person appointments, ensuring that patients receive comprehensive support in managing their sensitivities effectively. Additionally, food sensitivities can develop later in life, making it crucial to stay informed about one’s health. As specialists note, recognizing the differences between gluten intolerance and grain sensitivity is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Identify Symptoms of Wheat Allergy in Adults
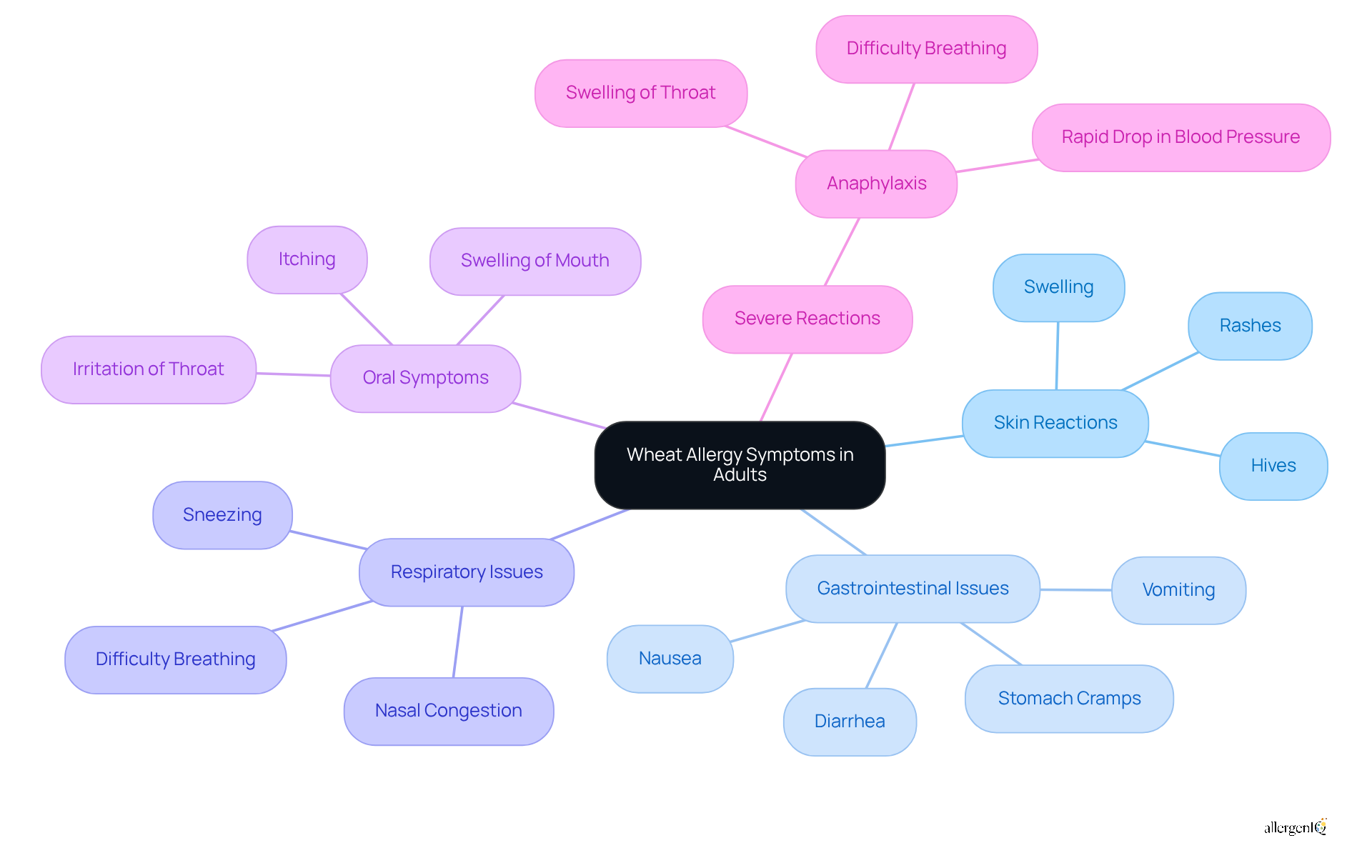
Recognizing the symptoms of wheat allergy in adults is crucial, as they can vary significantly among individuals for effective management. Common symptoms include:
- Skin Reactions: Individuals may experience hives, rashes, or swelling, which can appear rapidly after exposure to wheat proteins.
- Gastrointestinal issues, which include symptoms of wheat allergy in adults like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps, are prevalent and can occur within minutes to 30 minutes after ingesting the grain.
- The symptoms of wheat allergy in adults can include respiratory issues such as nasal congestion, sneezing, and difficulty breathing, which may escalate quickly in sensitive individuals.
- Oral symptoms, including swelling, itching, or irritation of the mouth or throat, can indicate an allergic response to grain, which may be among the symptoms of wheat allergy in adults.
- In severe cases of systemic reactions, the symptoms of wheat allergy in adults may include anaphylaxis, which is characterized by difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, and a rapid drop in blood pressure. This life-threatening reaction necessitates immediate medical attention and is a critical concern for adults who may have previously consumed grain without issues.
It is essential to understand that sensitivity to grain differs from celiac disease, which involves an autoimmune reaction to gluten. Recent studies indicate that sensitivity to grains affects millions of Americans, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Anaphylaxis, a severe allergic response, is particularly concerning, as it can occur within seconds of exposure and may impact multiple body systems. It is vital for adults to understand the symptoms of wheat allergy in adults, especially those who might develop a sensitivity to wheat later in life.
At AllergenIQ, we stress the importance of recognizing skin reactions and gastrointestinal distress, as these can significantly affect daily activities and overall well-being. Our comprehensive food allergy testing process includes a detailed online questionnaire followed by a virtual consultation with our allergy specialists. This approach ensures that individuals receive a personalized treatment plan tailored to their specific triggers. Regular discussions with healthcare professionals, including assessments such as IgE antibody testing, the Skin Prick Test, and Blood Test, can aid in managing these symptoms effectively, ensuring individuals are prepared to respond to allergies promptly. Furthermore, those with serious sensitivities should carry emergency medication, such as an epinephrine auto-injector, to address potential anaphylactic reactions.
Explore Diagnostic Procedures for Wheat Allergy
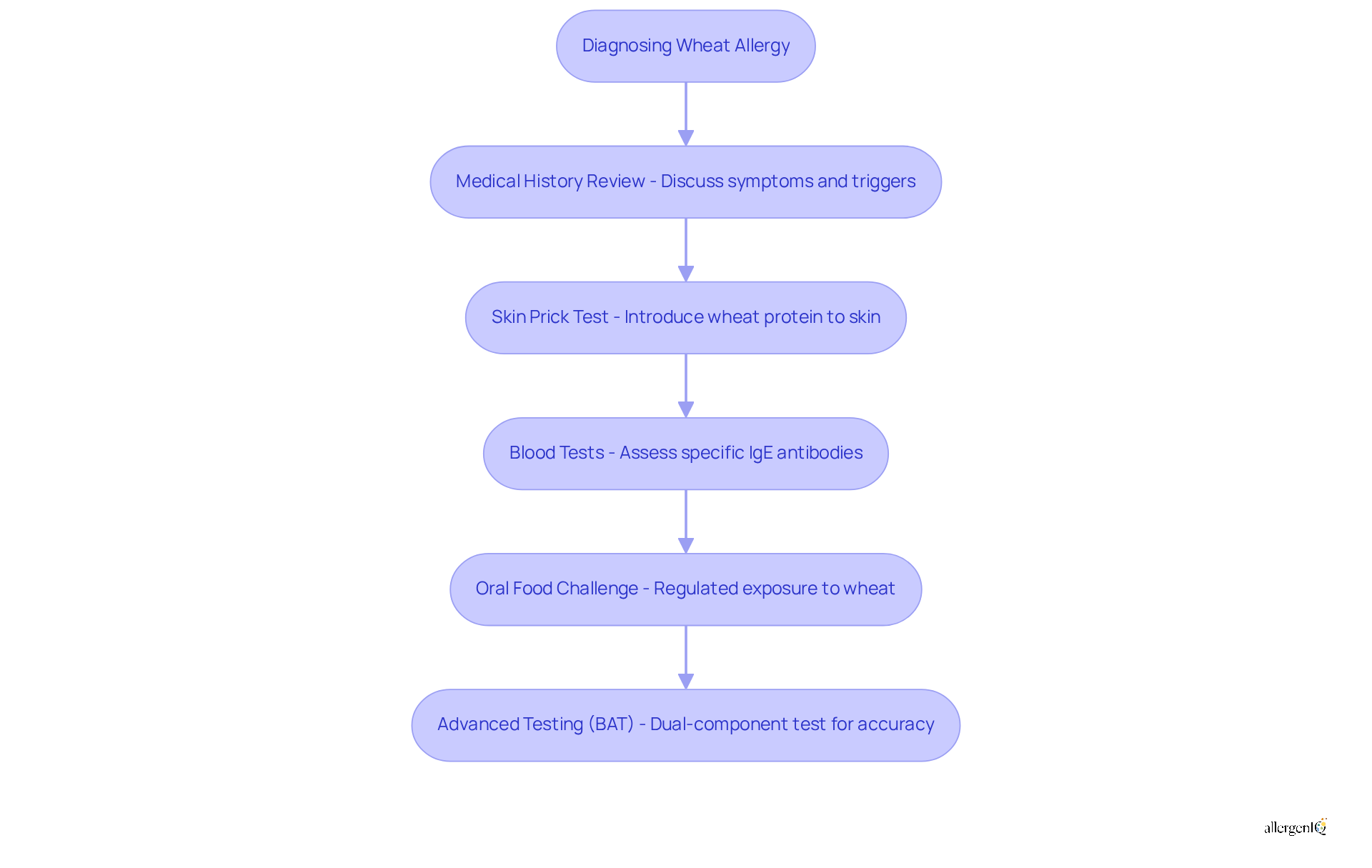
Diagnosing wheat allergy involves a systematic approach that includes several key steps:
-
Medical History Review: A detailed discussion of the symptoms of wheat allergy in adults and their potential triggers is essential. This helps healthcare providers understand the patient's experience and identify patterns that may indicate the symptoms of wheat allergy in adults. At AllergenIQ, we emphasize the importance of this initial step to tailor our personalized treatment plans effectively, facilitated through our streamlined virtual consultation process.
-
Skin Prick Test: This widely used method involves introducing a small amount of wheat protein to the skin. The test is effective in identifying allergic reactions, with current data indicating a sensitivity of approximately 73% and specificity of 73%. While the test is reliable, it may not be definitive on its own. AllergenIQ employs this method along with other diagnostic tools to ensure thorough care for sensitivities.
-
Blood Tests: These tests assess specific IgE antibodies to grain proteins, offering further validation of the allergy. Increased amounts of wheat-specific IgE can suggest a greater probability of allergic responses, with levels exceeding 100 kU/L linked to a 100% positive predictive value for clinical reactivity. Our science-backed approach at AllergenIQ ensures that these tests are part of our thorough evaluation process, enhancing the accuracy of our findings.
-
Oral Food Challenge: In specific instances, a regulated exposure to grain under medical oversight may be carried out. This approach is regarded as the gold standard for diagnosing grain sensitivities, permitting direct observation of reactions. At AllergenIQ, we coordinate support for patients undergoing this challenge to ensure safety and accuracy.
These diagnostic techniques are essential for precisely recognizing gluten intolerance and distinguishing it from other conditions, such as non-celiac gluten sensitivity or celiac disease. Recent advancements, including the dual-component basophil activation test (BAT), have shown promise in enhancing diagnostic accuracy, particularly for complex cases like wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis (WDEIA). The BAT has demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity when using component allergens like ω-5 gliadin and HMW-glutenin. By utilizing a mix of these methods, healthcare providers can offer personalized management strategies for individuals impacted by gluten sensitivities. As Dr. [Allergist's Name] states, "The skin prick test remains a cornerstone in diagnosing sensitivities, providing valuable insights into patient reactions.
Implement Management Strategies for Wheat Allergy
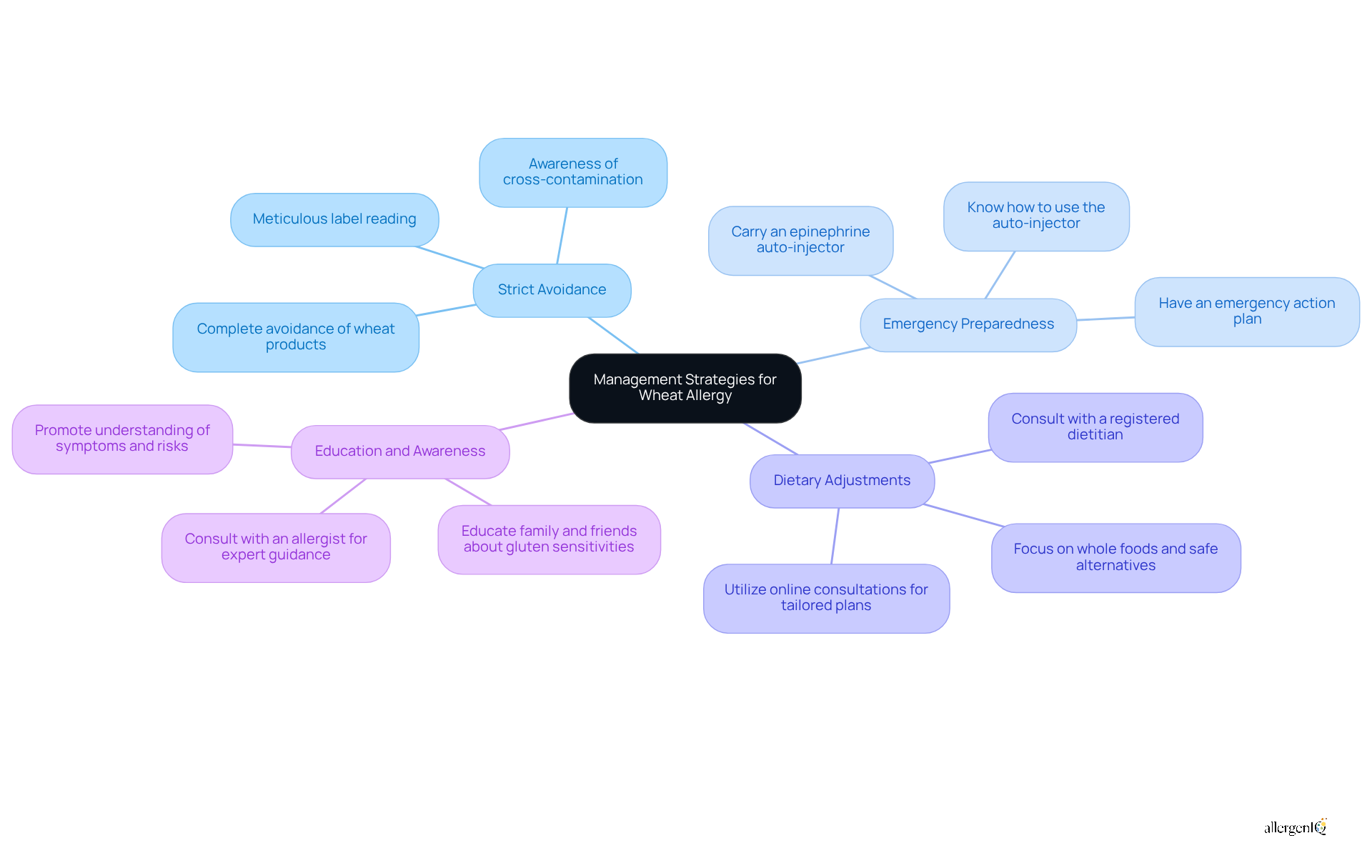
Managing the symptoms of wheat allergy in adults requires a comprehensive approach that prioritizes safety and well-being.
-
Strict Avoidance: The foundation of preventing allergic reactions lies in the complete avoidance of wheat and wheat-containing products. This requires meticulous label reading and an awareness of cross-contamination, as even trace amounts can trigger severe responses.
-
Emergency Preparedness: Individuals with gluten intolerance should consistently carry an epinephrine auto-injector. This is vital for addressing potential anaphylactic reactions promptly, as epinephrine is the only medication capable of reversing life-threatening symptoms.
-
Dietary Adjustments: Collaborating with a registered dietitian can facilitate the creation of a balanced diet that excludes gluten while meeting nutritional needs. Dietitians typically recommend focusing on whole foods and alternatives that provide essential nutrients without compromising safety. Additionally, AllergenIQ offers online consultations to assist individuals with gluten sensitivities in developing tailored dietary plans that cater to their specific requirements.
-
Education and Awareness: Enhancing understanding among family, friends, and colleagues regarding gluten sensitivities fosters a supportive environment and mitigates the risk of unintentional exposure. Education is crucial, as many individuals may not recognize the symptoms of wheat allergy in adults or the importance of avoiding gluten. Consulting with an allergist, such as those available through AllergenIQ's virtual services, is also advisable for concerns related to gluten sensitivity, ensuring individuals receive expert guidance in managing their condition.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can effectively manage their wheat allergy, promoting a healthier and safer lifestyle. Real-life examples demonstrate that strict adherence to these guidelines not only prevents allergic reactions but also enhances overall quality of life, supported by the expert care and personalized treatment plans available through AllergenIQ.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of wheat allergy in adults is essential for effective management and an improved quality of life. This article has clarified the distinctions between wheat allergy, gluten intolerance, and celiac disease, highlighting the necessity of precise diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. Recognizing the unique symptoms and triggers associated with wheat allergy is particularly important for adults, as sensitivities can develop later in life.
Key insights include a range of symptoms, from skin reactions to gastrointestinal distress, alongside systematic diagnostic procedures such as:
- Medical history reviews
- Skin prick tests
- Blood tests
Furthermore, effective management strategies - like strict avoidance of wheat, emergency preparedness, and dietary adjustments - are crucial for individuals navigating this condition. The role of education and support from healthcare professionals is paramount, empowering individuals to maintain their health and well-being.
Ultimately, awareness and proactive management of wheat allergy are critical for those affected. By prioritizing education, utilizing diagnostic resources, and implementing personalized treatment plans, individuals can take control of their health and significantly reduce the risk of allergic reactions. Embracing these strategies fosters a safer living environment and enhances overall wellness, underscoring the significance of understanding wheat allergy in adult health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is wheat allergy and how does it differ from celiac disease?
Wheat allergy is an immune reaction to cereal proteins, characterized by an IgE-mediated response that causes symptoms in adults. In contrast, celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder affecting about 1% to 2% of the U.S. population, primarily women, where gluten consumption leads to the immune system attacking the small intestine's villi, causing malabsorption and various symptoms.
What is non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS)?
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) is a condition where individuals experience symptoms related to gluten consumption but do not have an immune reaction or celiac disease. It affects about 10% of individuals without celiac disease or grain intolerance and can cause symptoms such as bloating, abdominal discomfort, and fatigue.
Why is it important to differentiate between wheat allergy, celiac disease, and gluten sensitivity?
Differentiating between these conditions is critical for effective treatment strategies. Celiac disease requires a strict gluten-free diet, while wheat allergy and NCGS may involve different management approaches. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment and complications.
What challenges exist in diagnosing non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS)?
Diagnosing NCGS is challenging due to its vague symptoms and the need to exclude other conditions. This complexity can lead to difficulties in identifying the condition accurately.
How can cross-reactivity between cereal grains and grass pollen affect diagnosis?
Patients sensitive to grass pollen may be misdiagnosed as allergic to cereal grains due to significant cross-reactivity between their proteins. This overlap can result in the over-diagnosis of wheat sensitivities and complicate effective management.
What services does AllergenIQ provide to help individuals with wheat allergies or sensitivities?
AllergenIQ offers at-home testing kits to help individuals identify specific allergens and provides online consultations that deliver the same quality of care as in-person appointments, ensuring comprehensive support for managing sensitivities.
Can food sensitivities develop later in life?
Yes, food sensitivities can develop later in life, making it important for individuals to stay informed about their health and any changes in their reaction to foods.




